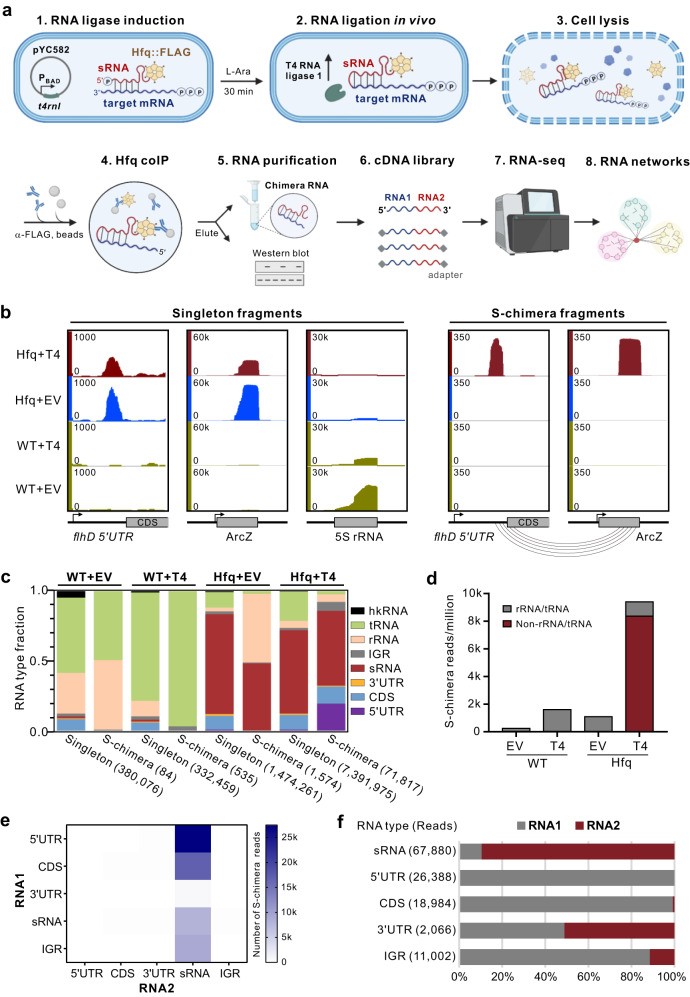
Fig. 1. iRIL-seq faithfully captures sRNA-target interactions.
a Schematic of iRIL-seq. Salmonella Hfq::FLAG strain carrying the plasmid pBAD-t4rnl1 (pYC582) was grown in LB. sRNA-target pairs were ligated to form chimeras in vivo by T4 RNA ligase induced for 30 min with L-arabinose. The ligation chimeras bound to 3xFLAG tagged Hfq were enriched using coIP from bacterial lysates. Chimeras were then purified, identified by deep sequencing, and used to determine the RNA interaction network by subsequent in silico analysis. Created with BioRender.com. b iRIL-seq captured known sRNA-target interactions. Genome browser screenshots showing the genomic locations of indicated RNAs covered by singleton or significant chimera reads (S-chimera, p < 0.05, one-sided Fisher’s exact test). Salmonella WT and Hfq::FLAG strains carrying empty vector or pYC582 were grown in LB. Bacteria were treated with L-arabinose for 30 min and grown to OD600 of 2.0. Cells were collected and performed iRIL-seq. EV: empty vector. T4: pBAD-t4rnl1 (pYC582). ORFs and RNAs were indicated by gray boxes. c Distribution of each transcript type for singleton and S-chimeric fragments within one set of four iRIL-seq libraries. The total number of sequenced fragments was denoted in parentheses. hkRNA: four housekeeping RNA (RnpB, SsrS, Ffs and SsrA). IGR: intergenic region. EV and T4 are the same as in (b). d Number of S-chimeric fragments detected in each sample. EV and T4 are the same as in (b). e Number of S-chimeric fragments for different transcript types. RNA1, the 5’ terminal RNA in the chimera. RNA2, the 3’ terminal RNA in the chimera. f Distribution of RNA1 and RNA2 in S-chimeras for different transcript types.