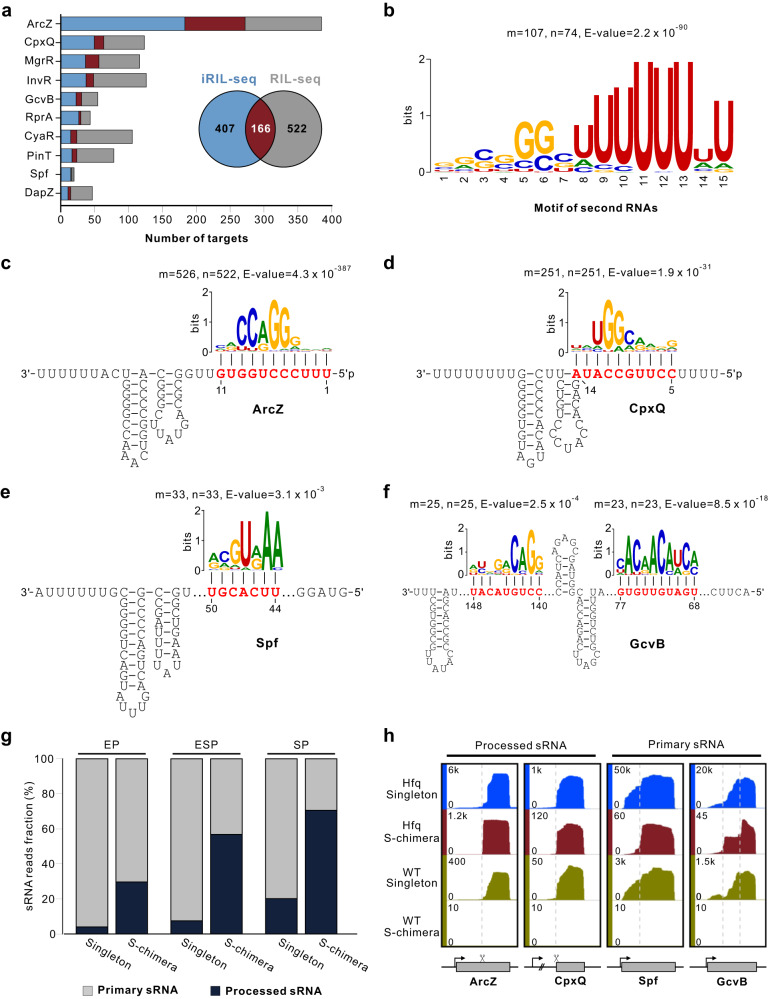
Fig. 3. Characterization of sRNA-target interactions in iRIL-seq datasets.
a Comparison of the sRNA-mRNA interactions found by iRIL-seq and RIL-seq under ESP condition. The bars indicate the numbers of predicted targets for 10 sRNAs that have most targets predicted. Venn diagram (inset) shows the overlap of all predicted targets for these 10 sRNAs between the two datasets. b Sequence motif identified in RNA2 in S-chimeras. M indicates the total number of RNA2 sequences. N indicates the number of RNA2 sequences containing the motif. c–f Motifs identified in the targets are complementary to the cognate sRNAs. m, the total number of target sequences. n, the number of target sequences containing the motif. g Known processed sRNAs (Supplementary Data 6) were enriched in S-chimeras compared to primary sRNAs. Similar trend was also observed by RIL-seq (Supplementary Fig. 3). h Genome browser screenshots showing the genomic locations of sRNAs as singleton and S-chimeric fragments in the iRIL-seq dataset at ESP. Dashed lines indicate the 5’ end of sRNA fragments found in S-chimeras in Hfq-associated iRIL-seq data.