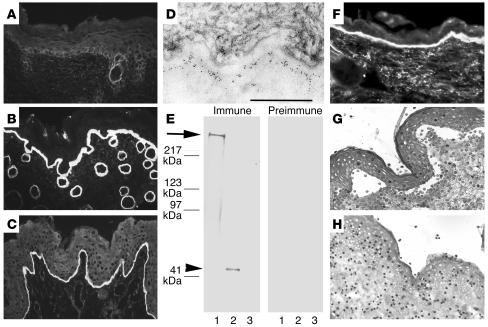
Figure 2.
Serum IgG from rabbit SA2954 binds to the DEJ, recognizes type VII collagen, and activates complement and leukocytes in vitro. IF microscopy of rabbit SA9254 serum on frozen skin sections shows no specific staining before immunization (A); in contrast, after immunization with type VII collagen, IgG binds to the DEJ of mouse (B) and human (C) skin (magnification, ×250). (D) By immunoelectron microscopy, IgG purified from immune rabbit serum binds to the lamina densa of mouse skin. Scale bar: 0.5 μm. (E) Extract of murine dermis (lane 1) and equimolar amounts of GST-mCOL7C (lane 2) and GST (lane 3) were separated by gradient 4–20% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with immune and preimmune rabbit serum preadsorbed against GST. IgG from immune serum, but not preimmune serum, binds to both full-length cell-derived (arrow) and recombinant fragment C (arrowhead) of type VII collagen. (F) Frozen murine skin sections were incubated with immune rabbit serum and subsequently with fresh serum as a source of complement. Bound murine C3 was visualized at the DEJ by FITC-labeled antibody (magnification, ×250). When incubated with frozen sections of human skin in the presence of human leukocytes, IgG from the immune (G), but not preimmune (H) rabbit–induced dermal-epidermal separation was observed (magnification, ×400).