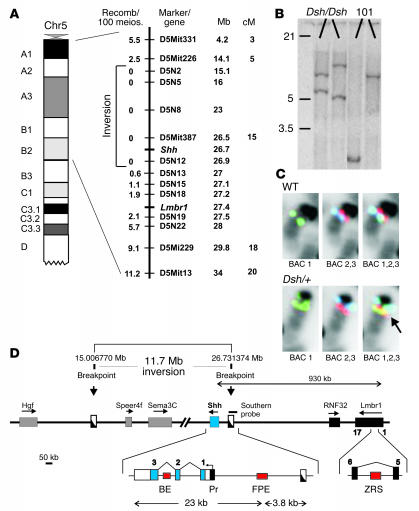
Figure 2.
Dsh is caused by an inversion involving the Shh gene. (A) Mapping of Dsh shows linkage to mouse chromosome 5 in a region containing Shh. A schematic of proximal chromosome 5 is shown on left. Enlargement of the indicated region shows the linkage interval with the marker tested, the Shh and Lmbr1 genes, and the number of recombinant mice observed per 100 meioses (Recomb/100 meios). Note repression of recombination in the inversion interval. Mb, megabase; cM, centi Morgan. (B) Southern blot analysis using a probe spanning the distal breakpoint showing aberrant bands in Dsh/Dsh mice. (C) Fluorescence in situ hybridization with BACs from mouse chromosome 5 that flank the inversion breakpoints. In the WT 3 colors are visible, in the order of red and green/blue (from centromere to telomere, BAC 1,2,3). In the Dsh mutant, BAC RP23-94F17 (green, BAC 1) shows a split signal and the order of telomeric and centromeric BACs is changed to blue/green and red/green (BAC 1,2,3), thus demonstrating the inversion. (D) Genomic region of the proximal and distal breakpoints. Genes are indicated by boxes, the direction of transcription is marked by arrow. FPE, floor plate enhancer; BE, brain enhancer; Pr, promoter; ZRS, regulatory element.