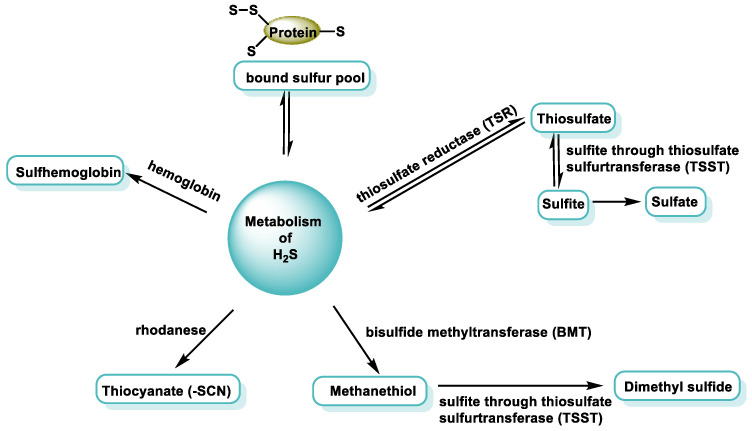
Figure 10.
The metabolic processes involved in the breakdown and utilization of H2S. H2S is degraded by various enzymatic reactions. The enzymes rhodanese, bisulfide methyltransferase (BMT) and thiosulfate reductase (TSR) play critical roles in catalyzing the conversion of H2S to thiocyanate, methanethiol and thiosulfate, respectively. Oxidation of thiosulfate to sulfite can occur through the enzymatic action of thiosulfate sulfurtransferase (TSST), followed by further oxidation to sulfate. H2S reacts with hemoglobin, resulting in the formation of sulfohemoglobin. In addition, H2S combines with proteins present in the tissue, resulting in the formation of a bound sulfur pool.