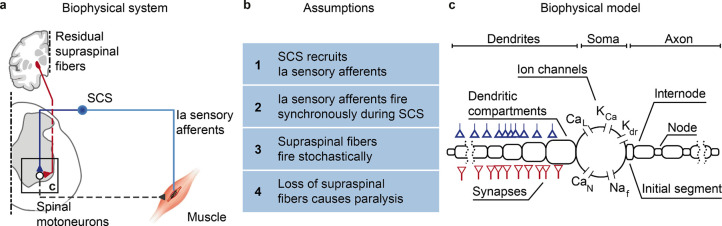
Fig. 1 |. Biophysical model with underlying assumptions.
a, Schematic of the spinal circuit involved in the recovery of voluntary movement during SCS composed of the monosynaptic Ia-to-motoneuron reflex circuit and supraspinal monosynaptic connections. Spinal motoneurons receive excitatory inputs from residual supraspinal fibers and Ia afferents recruited by SCS. b, Four assumptions grounded on experimental evidence that constitute the biophysical model of spinal motoneurons. c, Three-element biophysical model: motoneuron, Ia afferents inputs and supraspinal inputs. Biophysical model of spinal alpha motoneuron encompasses an electronic-equivalent dendritic tree, multicompartment soma and myelinated axon, connected through an initial axon segment. Motoneuron membrane dynamics follow dedicated Hodgkin–Huxley equations for multiple ion channels: L-type Ca2+, Ca2+-activated K, delayed rectifier K+, N-type Ca2+, and nonlinear fast Na+.