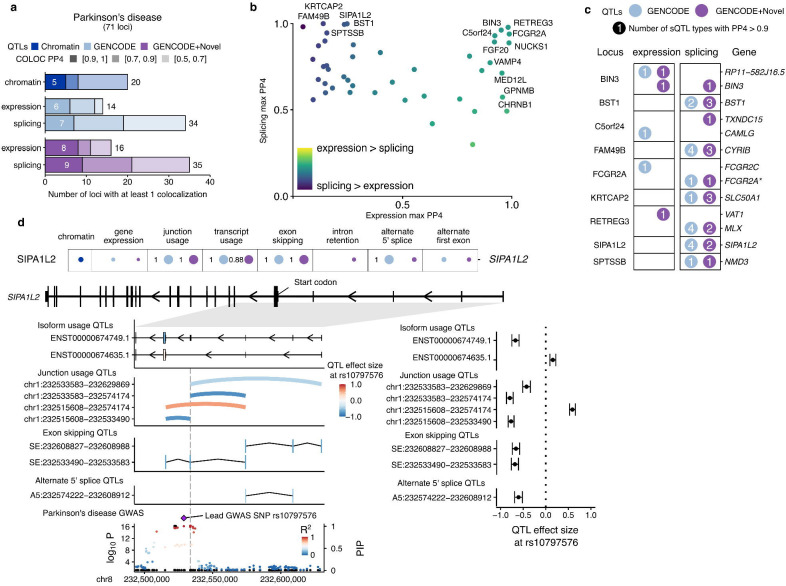
Fig. 6 |. Splicing QTLs in Parkinson’s disease identifies 5’UTR exon in SIPA1L2.
a, Colocalization discovery rate for microglia chromatin, expression and splicing QTLs in Alzheimer’s disease at different thresholds of colocalization posterior probability (PP4). “Splicing” represents a combination of all 8 sQTL modalities. b, Comparing the maximum expression and splicing PP4 for each locus across both references. Labels refer to loci with PP4 > 0.9. c, Colocalization results at each locus in Parkinson’s disease with at least one colocalized sQTL at PP4 > 0.9. Numbers within circles refer to the number of different sQTL modalities with a colocalization PP4 > 0.9. Asterisks refer to additional genes being implicated in fusion isoforms and/or overlapping splice junctions. d, Splicing QTL colocalizations at the SIPA1L2 locus implicate a non-coding cassette exon in the 5’UTR. Colocalization posterior probabilities (PP4) in each QTL modality in the two references. Values without numbers are PP4 <0.5. Isoform usage, junction usage and splicing event QTLs converge on the difference in inclusion of fourth 5’UTR exon upstream of the start codon (left panels) with effect sizes relative to the lead GWAS SNP in the SIPA1L2 locus (right panels). The SIPA1L2 GWAS locus in Parkinson’s disease contains multiple SNPs in high LD overlapping or nearby exon 4 (vertical dotted line). Black dots denote fine-mapping PIPs (right axis), whereas coloured dots refer to the −log10(P-value) of the GWAS (left axis). PIP: Posterior inclusion probability.