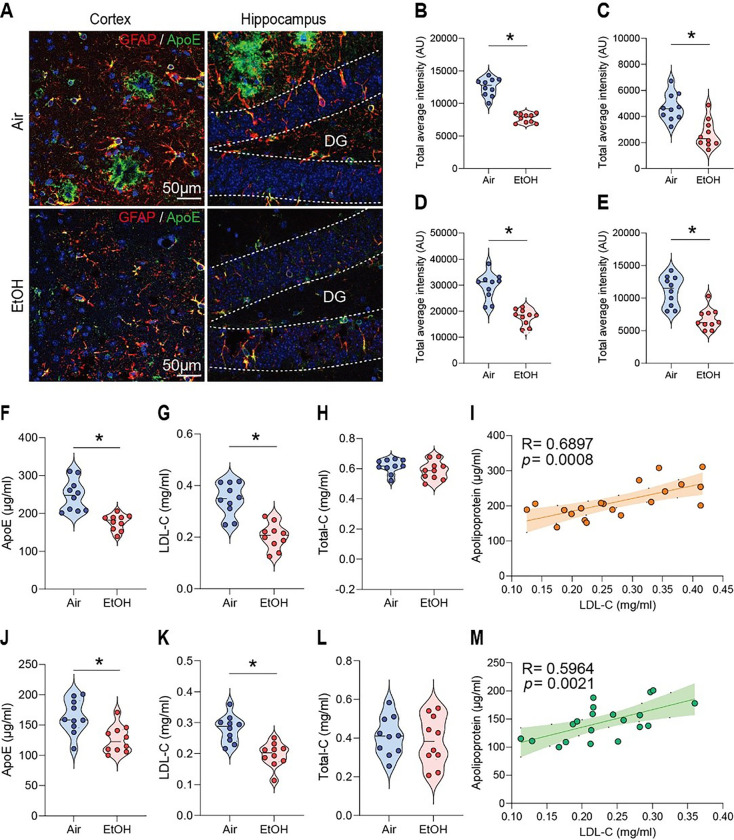
Figure 1.
Impact of moderate ethanol exposure on ApoE and LDL cholesterol levels in the brains of presymptomatic APP/PS1 mice. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ApoE (green) and GFAP (red) co-staining in the brains of air-exposed and ethanol-exposed APP/PS1 mice. (B and C) ApoE IHC evaluation revealed reduced ApoE levels in the cortex (B) and hippocampus (C) compared to the air-exposure group. (D and E) GFAP IHC evaluation showed decreased astrocyte activation in the cortex (D) and hippocampus (E) in the ethanol exposure compared to the air group. (F-H and J-L) Analysis of ApoE, LDL-cholesterol, and Total-cholesterol levels in the cortex and hippocampus by ELISA after moderate ethanol exposure. (F) ApoE level in the cortex, (G) LDL-cholesterol level in the cortex, (H) Total cholesterol level in the cortex, (I) Correlation in the cortex, (J) ApoE level in the hippocampus, (K) LDL-cholesterol level in the hippocampus, (L)Total cholesterol level in the hippocampus. (M)Correlation in the hippocampus. Data represent mean ± SEM; n= 10 per group. *P < 0.05 comparing each group. (B-l and K-N) Two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. (I and M) Spearman correlation analysis. Linear regression (solid line) and 95% confidence bands (shaded are) are shown. See Table S1 for full statistical information.