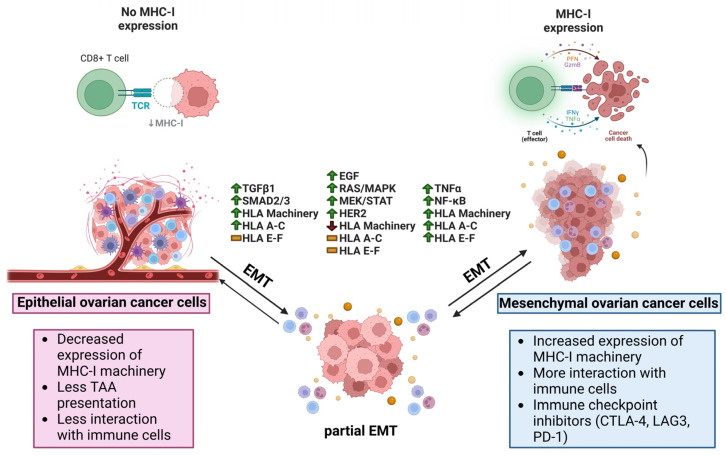
Figure 5.
Potential relationship between antigen presentation and EMT in ovarian cancer. In ovarian cancer, epithelial cancer cells have decreased expression of classical HLA I related machinery, less interaction with immune cells, and less TAA presentation. Once stimulated with TGF-β1, EMT can begin increasing the expression of EMT-TFs such as SNAIL, SLUG, ZEB1, and TWIST1/2. At the same time, SMAD2/3 pathways are active, leading to the activation of APM and the re-expression of HLA-A, -B, and -C, and further leading to increased immunogenicity as the cells undergo EMT. If the EGF receptor (EGFR) is stimulated, the cells begin to undergo an EMT coinciding with activation of the RAS/MAPK, MEK/STAT, and HER2 pathways while seeing a reduction in APM and no changes to typical and atypical HLA I allotypes. EMT also beings if cancer cells are stimulated by TNF-α, including an increase in NF-κB that is upstream of APM and both typical and atypical HLA molecules. With increased immunogenicity in the mesenchymal phenotype as a result of more antigen presentation, immune cells like CD8+ T cells are able to effectuate their cytolytic functions on the cancer cells through PFN, GZMB, IFN-γ, and TNF-α. TAA (Tumor associated antigen), TGF-β1 (Transforming growth factor β1), EMT-TF (Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factor), SNAIL (Zinc finger protein SNAI1), SLUG (Zinc finger protein SNAI2), ZEB1 (Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox1), TWIST1/2 (Twist-related protein 1/2), SMAD2/3 (Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2/3), APM (Antigen presenting machinery), HLA (Human leukocyte antigen), EGF (Epidermal growth factor), RAS/MAPK (Reticular activating system/Mitogen-activated protein kinase), MEK/STAT (Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/Signal transducer and activator of transcription), HER2 (Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2), EMT (Epithelial-mesenchymal transition), NF-κB (Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells), PFN (Perforin), GZMB (Granzyme B), IFN-γ (Interferon gamma).