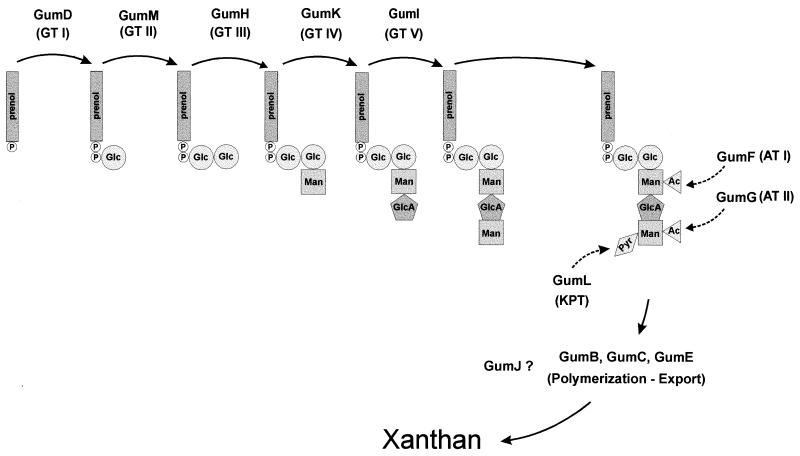
FIG. 7.
Scheme of the proposed gum gene functions for the biosynthesis of the exopolysaccharide xanthan in X. campestris. The components of the lipid-linked intermediates are represented as follows: Glc, glucose; Man, mannose; GlcA, glucuronic acid; Ac, acetyl group; Pyr, pyruvyl group. The designation of each protein is followed by its proposed function as follows: GT, glycosyltransferase; AT, acetyltransferase; KPT, ketal pyruvate transferase. Dashed arrows indicate that repeating units are variably decorated. GumJ could not be associated with any particular gum biosynthetic step, although the possibility of its participation in pre- or postpolymerization processes cannot be eliminated (see text).