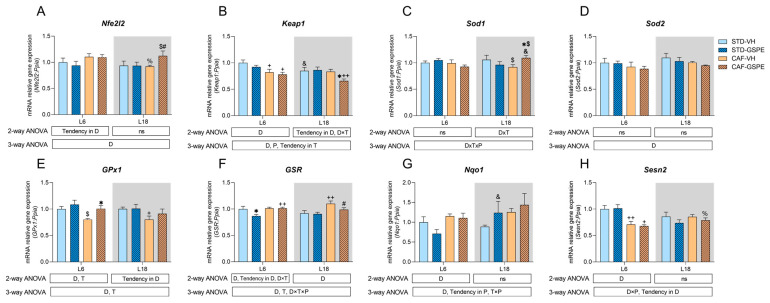
Figure 2.
Antioxidant-related relative gene expression in the liver. All data were relativized to the L6-STD-VH group: (A) nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (Nfe2l2); (B) Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1); (C) superoxide dismutase 1 (Sod1); (D) superoxide dismutase 2 (Sod2); (E) glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPx1); (F) glutathione-disulfide reductase (GSR); (G) NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone 1) (Nqo1); (H) Sestrin-2 (Sesn2). Values are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.; n = 4–6 for the L6 and L18 conditions. The statistical analyses were performed using 2- and 3-way ANOVAs. The letters D, T, and P refer to diet (STD vs. CAF), treatment (VH vs. GSPE), and photoperiod (L6 vs. L18) effect, respectively. An LSD post hoc test was used to compare between groups: $ (0.1 < p < 0.05), + (p < 0.05), and ++ (p < 0.01) indicate differences by diet effect; # (0.1 < p < 0.05) and * (p < 0.05) indicate differences by treatment effect; % (0.1 < p < 0.05) and & (p < 0.05) indicate differences by photoperiod effect. ns, indicates no significance; STD, indicates standard diet-fed rats; CAF, indicates cafeteria diet-fed rats; VH, indicates rats administered vehicle; GSPE, indicates rats were administered with grape seed proanthocyanidin extract at 25 mg/kg b.w.; L6, indicates short photoperiod with 6 h light per day; L18, indicates long photoperiod with 18 h light per day.