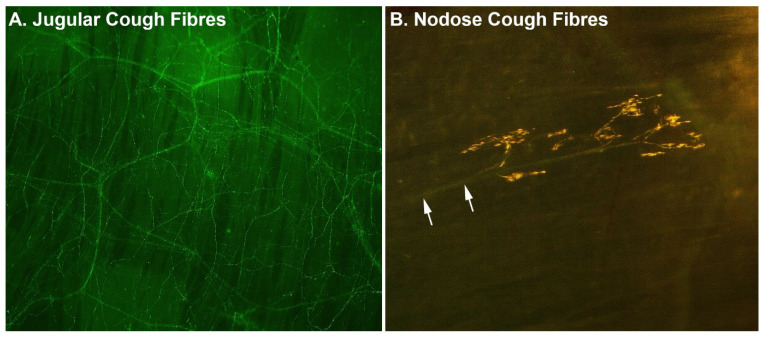
Figure 1.
Examples of (A) jugular and (B) nodose cough-evoking nerve fibres in the trachea. Images show representative stains of nerve fibres viewed from the luminal surface in tissue wholemounts collected from guinea pigs. Jugular cough neurons form a dense subepithelial plexus, with fibre branches extending between epithelial cells all the way to the luminal surface. By contrast, nodose cough mechanosensors are sparse and characteristically display a distinct parent axon (arrows), which ramifies into a complex subepithelial nerve ending. Comparable structures have been identified in human airways.