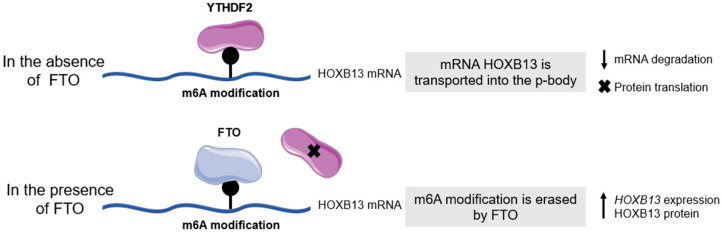
Figure 4.
m6A modification in HOXB13 mRNA in the absence and presence of FTO. The dynamic landscape of m6A modifications within HOXB13 mRNA reveals an intriguing dichotomy that hinges on the presence or absence of FTO. In the absence of FTO, the m6A modification attracts the binding of the YTHDF2 protein. This interaction orchestrates the translocation of mRNA to the p-body, a process that expedites mRNA degradation while simultaneously impeding the translation of proteins. In a distinct scenario where FTO is a participant, its presence holds the key to a transformative change. Acting as a molecular recognition system, FTO identifies the m6A modification and initiates a catalytic cascade, ultimately leading to the demethylation of the modification. This orchestrated demethylation event serves as a trigger, ushering in an upsurge in the expression of HOXB13. This intricate regulatory mechanism highlights the pivotal role of FTO in orchestrating a finely tuned balance between mRNA degradation and the augmentation of protein synthesis within the context of HOXB13 expression. (×) absence of YTHDF2.