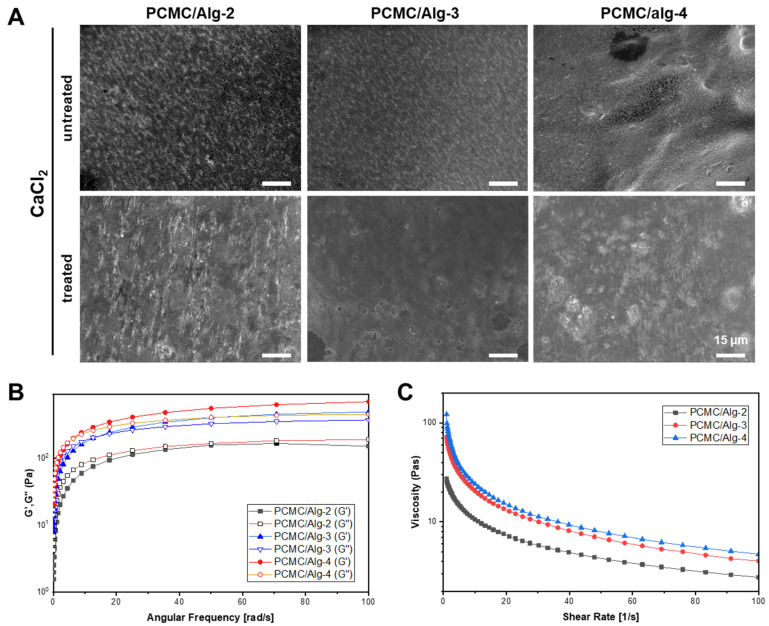
Figure 3.
Characterization of PCMC/Alg bioink. (A) Morphological analysis of PCMC/Alg bioink by SEM. A comparison was made between images before and after cross-linking using CaCl2, and the surface of PCMC/Alg was evaluated based on the alginate content. PCMC/Alg-2 and PCMC/Alg-3 exhibited a consistent distribution of alginate. After cross-linking with CaCl2, both retained residual porosity. In contrast, PCMC/Alg-4 showed an excess distribution of alginate on the surface, resulting in complete pore closure as an outcome of the cross-linking process. (B) Evaluation of the elastic properties of PCMC/Alg. Storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) were evaluated as a function of alginate content. (C) Evaluation of shear-thinning behavior. PCMC/Alg exhibited characteristics similar to those of hydrogels. PCMC/Alg bioinks exhibited shear-thinning behavior, expecting reduced shear stress during bioprinting with encapsulated cells.