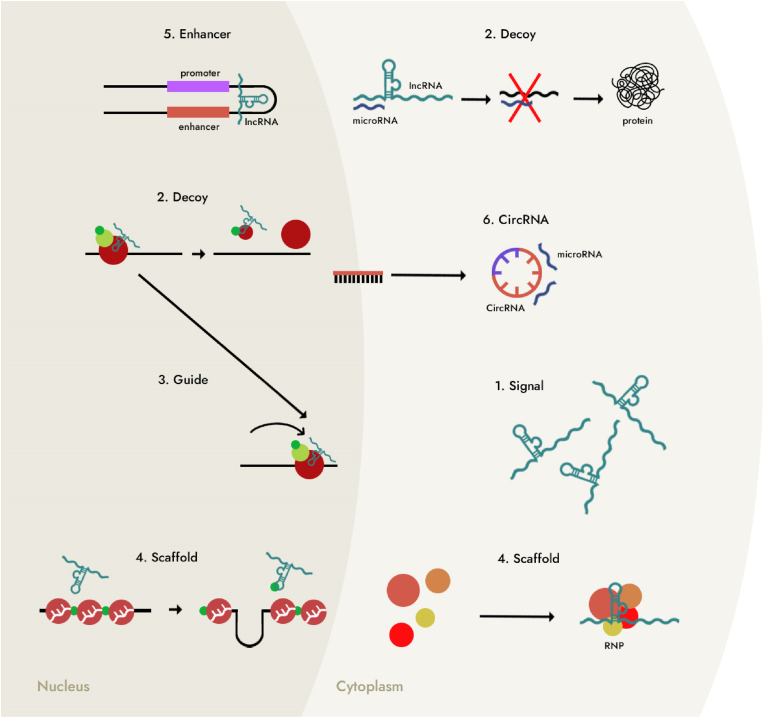
Fig. 1.
Presents the various functions attributed to long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). These functions can be categorized as follows: Signal lncRNAs: These lncRNAs are expressed at specific time points and in specific cellular locations, indicating their involvement in temporal and spatial signaling events. Decoy lncRNAs: These lncRNAs could bind to regulatory factors and microRNAs, altering their normal function and potentially modulating gene expression. Guide lncRNAs: These lncRNAs play a role in regulating gene activation or repression by facilitating the relocation of ribonucleoprotein complexes within the cell. Scaffold lncRNAs: Like guide lncRNAs, scaffold lncRNAs also facilitate the formation of ribonucleoprotein complexes; however, they primarily affect the molecular components of the complex itself. Enhancer lncRNAs: Produced from enhancer elements, these lncRNAs influence the activation of target genes by modulating enhancer-promoter interactions. Circular lncRNAs: Circular lncRNAs can interfere with various RNA processing and splicing events, and they can also act as sponges for microRNAs, sequestering them and preventing their regulatory functions.