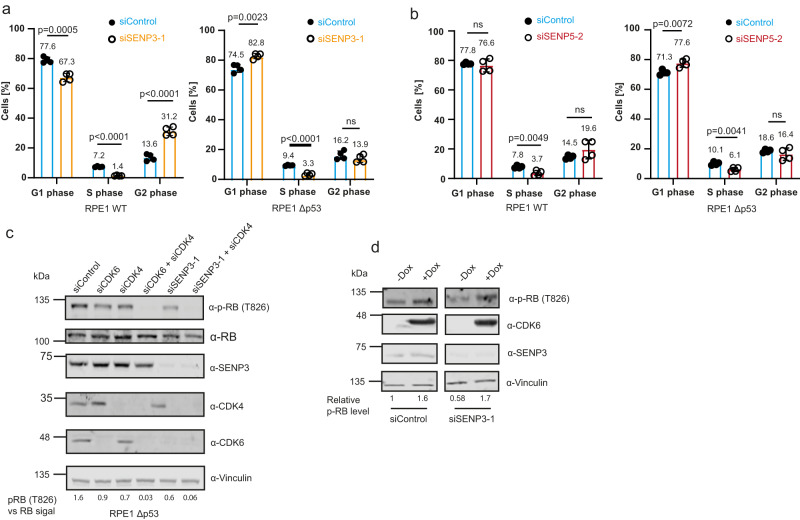
Fig. 7. SENP3 and SENP5 deficiency induces impairment of cell cycle progression in a CDK6/RB-dependent pathway.
a PI staining and cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry of parental RPE1 (left) or RPE1Δp53 (right) cells transfected with siSENP3 (orange) or siControl (blue) for 72 h. Percentage of G1, S or G2 phase cells was determined. Significance was determined by two-sided t-tests. Experiments were performed with four replicates and are shown as mean ± standard deviation. Mean values of the percentages are added above the bars. b PI staining of SENP5 depleted parental RPE1 (left) or RPE1Δp53 (right) cells performed as in (a). Significance level was calculated by two-sided t-testing. Experiments were performed with four replicates and are shown as mean ± standard deviation. Mean values of the percentages are added above the bars. c Immunoblot analysis of RPE1Δp53 cells transfected for 72 h with siRNAs as indicated. Antibodies were used as indicated. The phospho-RB as well as the RB level were quantified using the LI-COR Image studio software. The ratio of pRB level against the whole RB level is indicated by the respective numbers. d U2OS cells expressing FLAG-CDK6 under a doxycycline-inducible promoter were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against SENP3 for 72 h. FLAG-CDK6 expression was induced by supplementing the media with doxycycline (0.05 µg/ml) 48 h before cell lysis. Immunoblots were performed as indicated. phospho-RB (T826) levels were quantified and normalized to non-induced conditions. Source data for (a)–(d) are provided as a Source Data file.