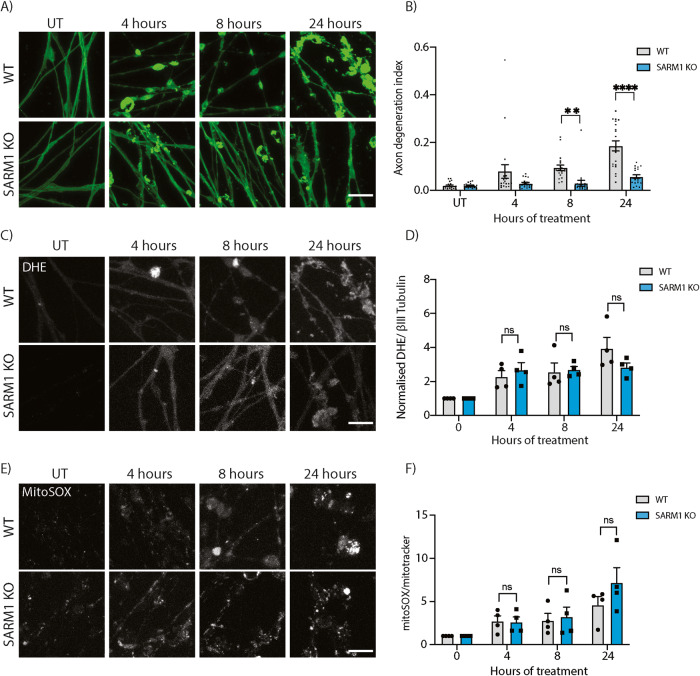
Fig. 6. SARM1 knockout prevents axon degeneration and does not prevent axonal and mitochondrial ROS production after vincristine treatment.
A Representative images of 5 nM vincristine-treated WT and SARM1 KO i3Neuron axons. Immunostaining for βIII tubulin (green). Scale bar = 20 µm. B Axonal degeneration index of the experiments shown in (A). Vincristine treated WT and SARM1 KO i3Neuron axons. Results are represented as mean ± SEM. N = 4 independent differentiations, 5 images per differentiation. Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni correction (p < 0.01 **, p < 0.0001 ****). C Representative images of 5 nM vincristine-treated WT and SARM1 KO neurons. Staining with DHE (white). Scale bar = 20 µm. D Quantification of DHE fluorescence in 5 nM vincristine WT and SARM1 KO i3Neuron axons shown in (C). Results normalized to untreated axons. Results are represented as mean ± SEM. N = 4 independent differentiations, 5–10 images per differentiation. Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni correction (ns not significant). E Representative images of 5 nM vincristine-treated WT and SARM1 KO i3Neuron axons ROS quantification. Staining with mitoSOX (white). Scale bar = 20 µm. F Quantification of mitoSOX fluorescence in 5 nM vincristine WT and SARM1 KO i3Neuron axons shown in (E). Results normalized to untreated axons. Results are represented as mean ± SEM. N = 4 independent differentiations, 5–10 images per differentiation. Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni correction (ns not significant).