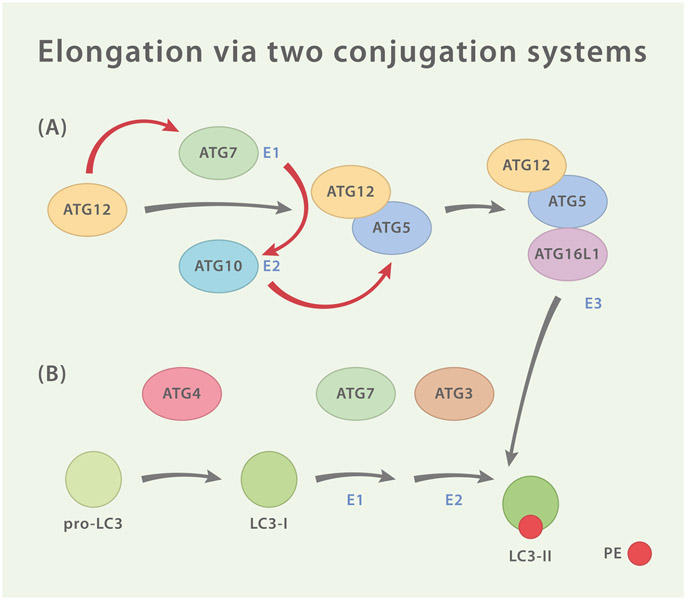
Fig. 3.
Two Ubiquitin-Like Conjugation Systems. (A) ATG12 is activated by homodimeric E1-like protein ATG7 and then transferred to E2-like protein ATG10 which catalyzes the covalent conjugation of ATG12 to ATG5. ATG16L1 associates with ATG5 and forms a tripartite conjugate which goes on to assemble tetrameric complexes with adjacent ATG5-ATG12/ATG16L1 conjugates (not shown). The complex is then recruited to the site of autophagogenesis by interaction of ATG16L1 with WIPI2 and/or FIP200. There, ATG5-ATG12/ATG16L1 functions as an E3-like enzyme for the second conjugation system (B) which consists of the ubiquitin-like LC3, the hydrolase ATG4, ATG7 and ATG3. ATG4 cleaves pro-LC3 resulting in LC3-I which exposes a C-terminal glycine. In order to generate LC3-II, this residue is then lipidated with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) by ATG7 (E1-like), ATG3 (E2-like) and ATG5-ATG12/ATG16L1 (E3-like).