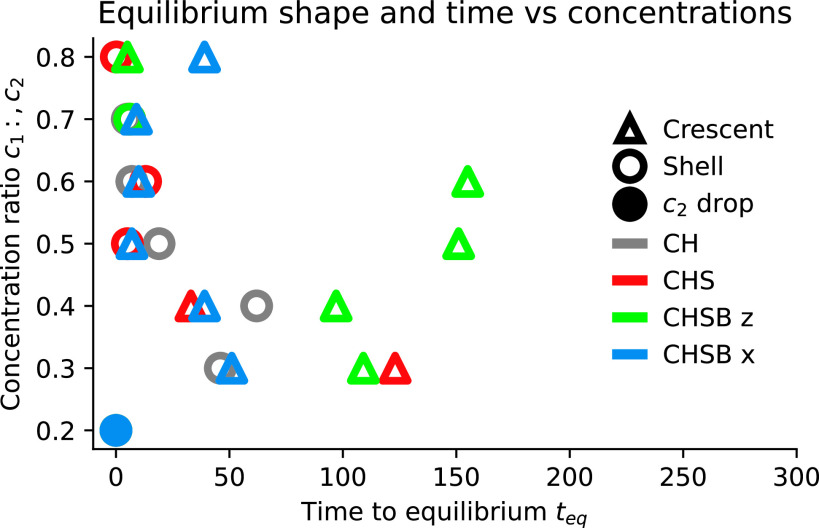
Fig. 6.
Equilibrium shape (Crescent , shell , and droplet ) and dimensionless time to equilibrium for CH (gray), CHS (red), CHSB (green), and CHSB (blue) models. Asymmetric buoyancy forces destabilize shell configurations, causing crescent formation. Pressure-driven pipe flow causes stronger recirculation, accelerating crescent formation by up to two orders of magnitude. Low concentrations instead diffuse out of the drop, leading to -only drops.