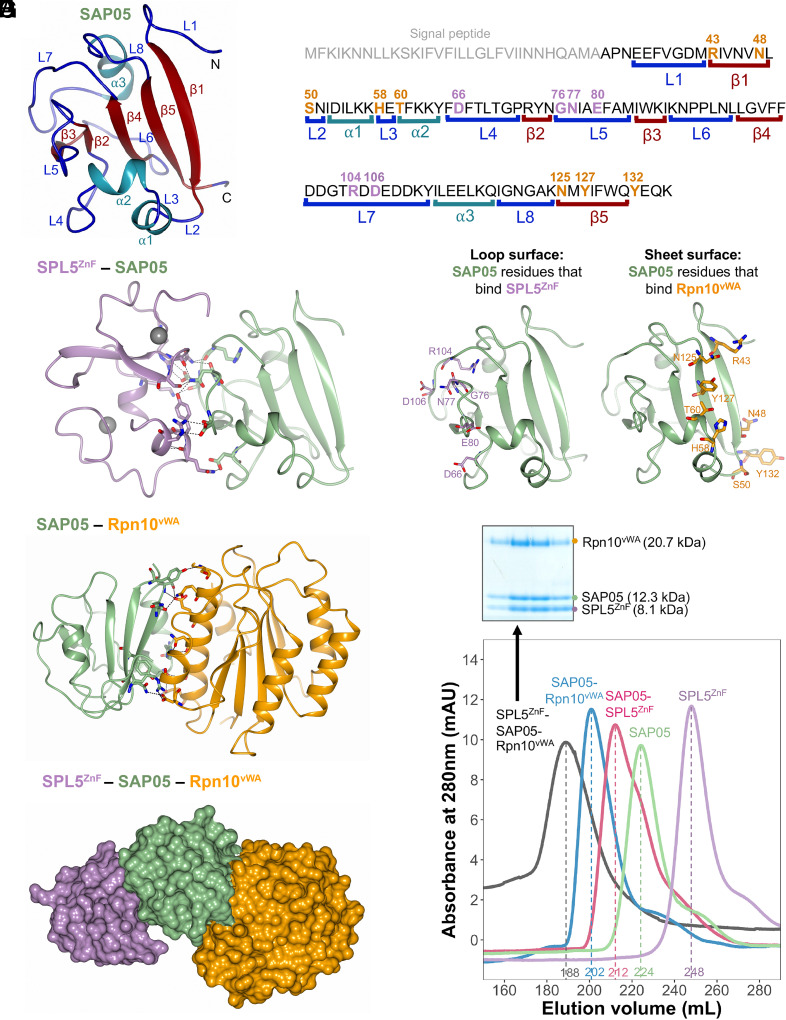
Fig. 1.
Crystal structures of SAP05–SPL5ZnF and SAP05–Rpn10vWA complexes revealing the bimodular architecture of SAP05. (A) Cartoon model illustrating the fold of the SAP05 effector. α-helices, β-sheets, and loops are indicated in cyan, red, and blue, respectively. (B) Amino acid sequence of SAP05 highlighting the locations of secondary structures (shown in A, color matched) and SPL5ZnF (purple) and Rpn10vWA interacting residues (orange) (shown in C–F, color-matched). SPL5ZnF, zinc-finger domain of SPL5 transcription factors. Rpn10vWA, von Willebrand factor type A domain of Rpn10 ubiquitin receptor. (C) Crystal structure of the SAP05–SPL5ZnF complex (PDB 8PFC). The Zn2+ ions bound to the two ZnF domains are shown in gray. (D) Crystal structure of the SAP05–Rpn10vWA complex (PDB 8PFD). In (C) and (D), the dashed lines indicate the interactions between the residues from both components. (E) Interfaces of SAP05 showing the loop surface (purple) and sheet surface (orange) residues that bind to SPL5ZnF and Rpn10vWA, respectively. (F) Gel filtration chromatograms of SAP05, SPL5ZnF, and Rpn10vWA and binary and ternary complexes of these proteins. The Coomassie-stained protein SDS-PAGE gel shows the presence of the three proteins in the SPL5ZnF–SAP05–Rpn10vWA ternary complex—see SI Appendix, Fig. S1, for the other complexes. Elution volumes are indicated at the bottom of each peak with the same colors. (G) Hypothetical ternary structure of SPL5ZnF–SAP05–Rpn10vWA obtained by superimposing the crystal structures of SAP05–SPL5ZnF and SAP05–Rpn10vWA complexes.