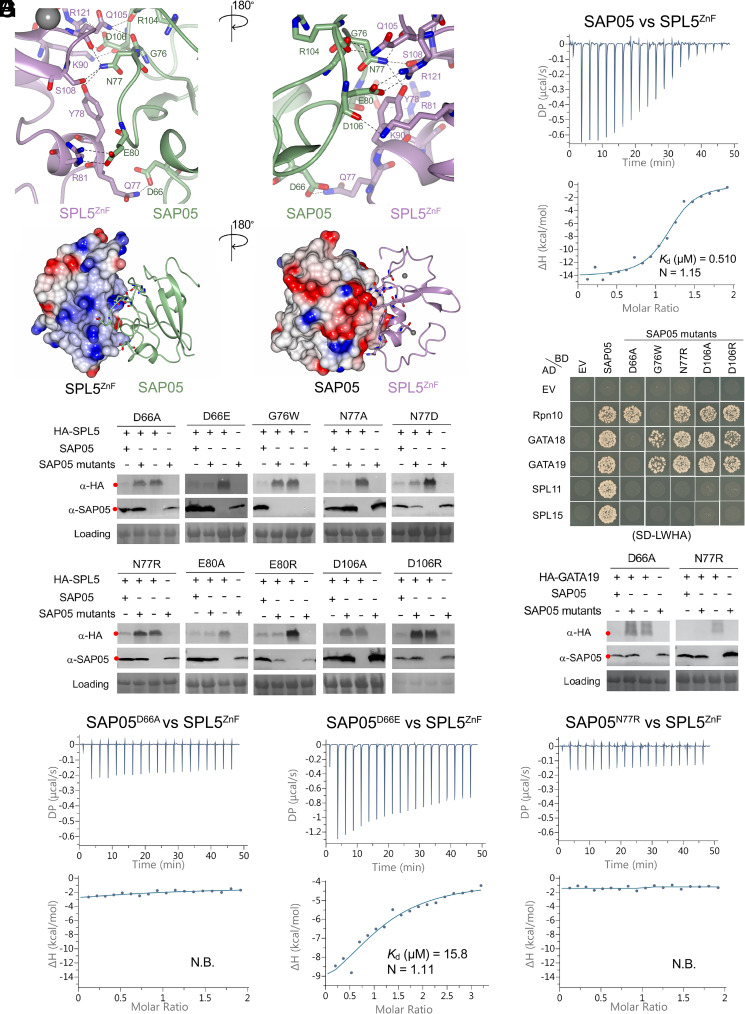
Fig. 2.
SAP05 loop surface interacts with SPL5ZnF. (A) Close-up views of SAP05–SPL5ZnF interaction interface from front (Left) and back (Right). The amino acid residues mediating electrostatic interactions are labeled. The Zn2+ ions are displayed as gray spheres. (B) Electrostatic potential surface view of SAP05 and SPL5ZnF during complex formation showing that the interacting interface is predominantly electronegative (red) in SAP05 and electropositive (blue) in SPL5ZnF. (C) ITC experiment showing direct physical binding of SAP05 and SPL5ZnF. (D) Western blot analysis of proteasomal degradation of SPL5 in the presence of wild-type or mutant SAP05 in N. benthamiana leaves. (E) Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assay to test interactions of SAP05 and its mutant versions with A. thaliana Rpn10 and GATA and SPL TFs. EV, empty vector control. AD, GAL4-activation domain. BD, GAL4-DNA binding domain. SD-LWHA, quadruple dropout medium lacking leucine, tryptophan, histidine, and adenine. Yeast growth on SD-LW medium is shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S6A. (F) Western blot analysis for GATA19 degradation in the presence of SAP05 D66A or N77R mutants in N. benthamiana leaves. In (D) and (F), red dots indicate the expected sizes of the transiently expressed proteins. HA, hemagglutinin. Protein loading was visualized using Ponceau S staining. (G) ITC titrations of three SAP05 mutants (D66A, D66E, and N77R) with SPL5ZnF. N.B., not binding. In (C) and (G), the top panels show heat differences upon interaction, and lower panels show integrated heats of injection (•) and the best fit to a single site binding model using MicroCal PEAQ-ITC analysis software. See SI Appendix, Fig. S5, for more ITC repeats and thermodynamic parameters.