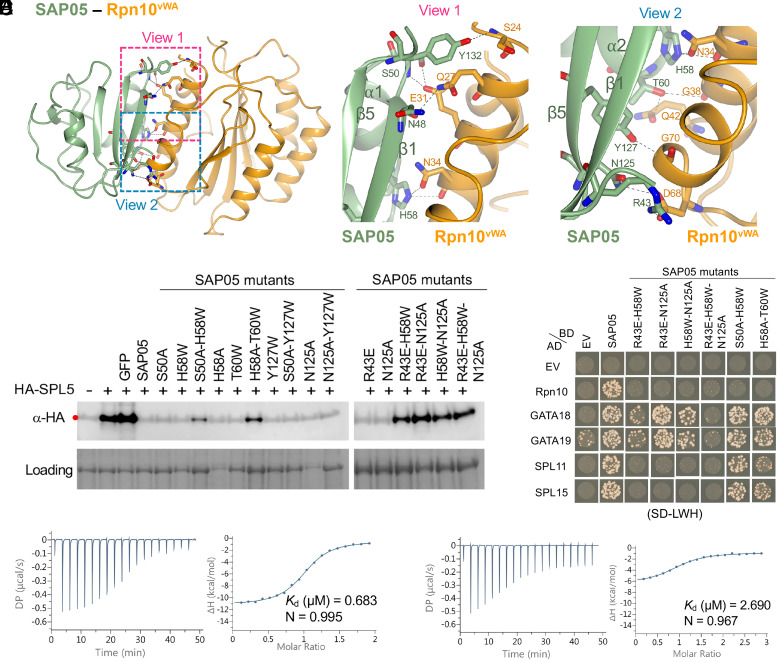
Fig. 3.
SAP05 β-sheet surface binds to Rpn10vWA. (A) Close-up views of SAP05–Rpn10vWA interaction interface showing the residues involved in complex formation. Left, overview of the interacting interface with two dashed squares displaying the areas for enlarged view. Middle, the enlarged view 1 of the top part in the interface. Right, the enlarged view 2 of the lower part in the interface. (B) Western blot analysis for SPL5 degradation with SAP05 wild-type and mutants in A. thaliana protoplasts. GFP, green fluorescent protein control. HA, hemagglutinin. Protein loading was visualized using Amido Black staining. (C) Y2H assay to test interactions of SAP05 and its mutants with A. thaliana Rpn10 and GATA and SPL TFs. EV, empty vector control. AD, GAL4-activation domain. BD, GAL4-DNA binding domain. SD-LWH, triple dropout medium lacking leucine, tryptophan, and histidine. See SI Appendix, Fig. S6B, for yeast growth on SD-LW medium. (D and E) ITC titrations of the SAP05–Rpn10vWA complex with SPL5ZnF (D) and SAP05H58A-T60W with SPL5ZnF (E). Left panels show heat differences upon interaction and right panels show integrated heats of injection (•) and the best fit to a single site binding model using MicroCal PEAQ-ITC analysis software. See SI Appendix, Fig. S5, for more ITC repeats and thermodynamic parameters.