Fig. 4.
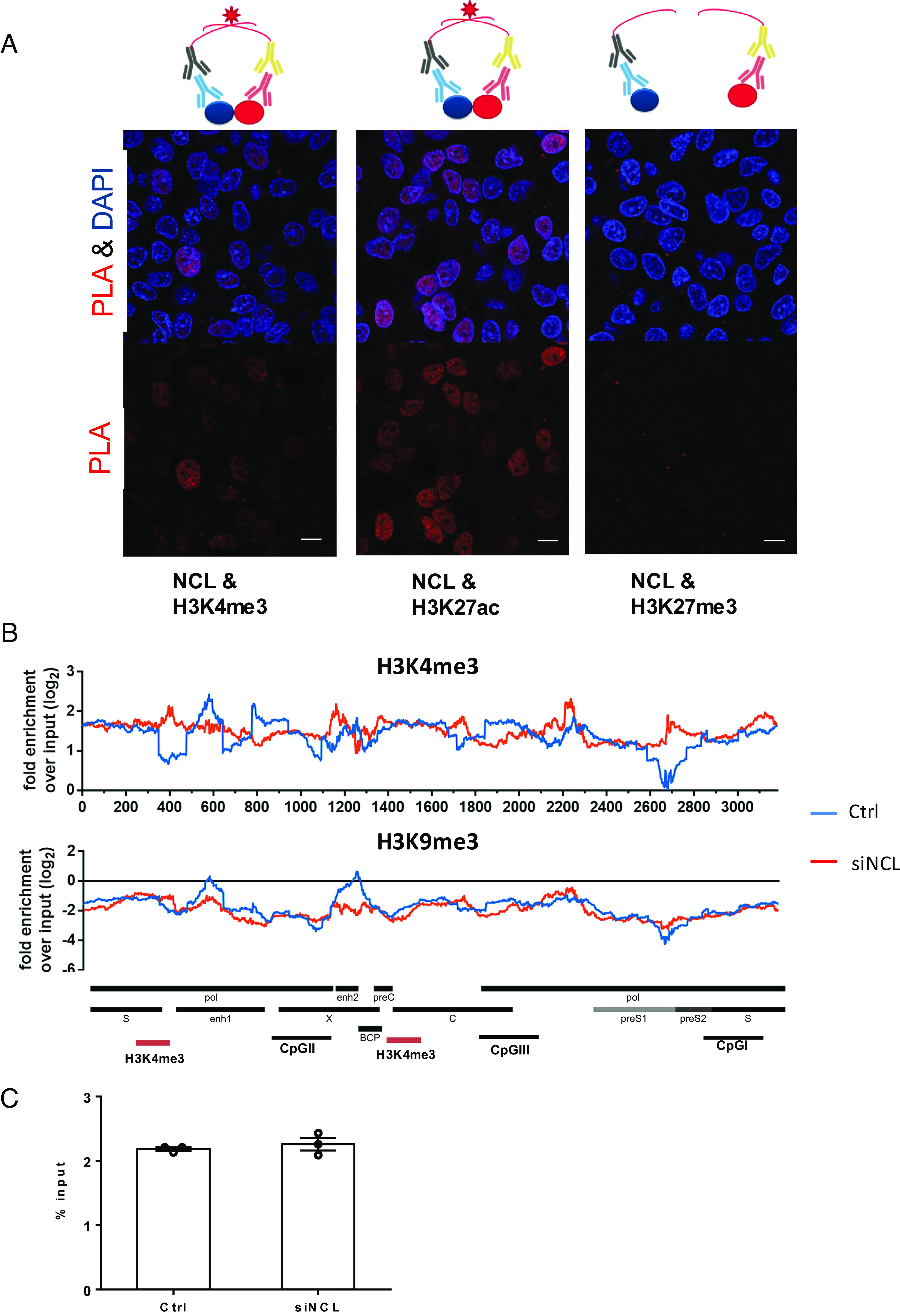
Interaction of nucleolin with HBV cccDNA. (A) Proximity ligation assay (PLA) to analyze the interaction of NCL and histones. The assay is schematically shown on the top of the figure. Antibodies against NCL or different histones were used in proximity ligation assay to determine their interaction in HBV-infected cells. HBV-infected HepG2-NTCP cells were fixed and incubated with NCL or histone antibodies. Secondary antibodies coupled with PLA probes were added and ligated. PLA signals are detected by fluorescent microscopy as discrete spots (in red) and provide the intracellular localization of the protein interaction (Scale bar, 10 μm). (B) Distribution of nucleosomes and H3K4me3 binding sites along the HBV genome in HBV-infected cells with or without NCL knockdown by ChIP-Seq. Read density for each track is represented by height on the y axis scaled to a minimum of 100 reads. Data are shown as fold-enrichment over input for each genome position, and various HBV genomic landmarks are displayed as in Fig. 3A. (C) The overall H3K4me3 signals on the HBV cccDNA were accessed by ChIP-qPCR and shown as % input.
