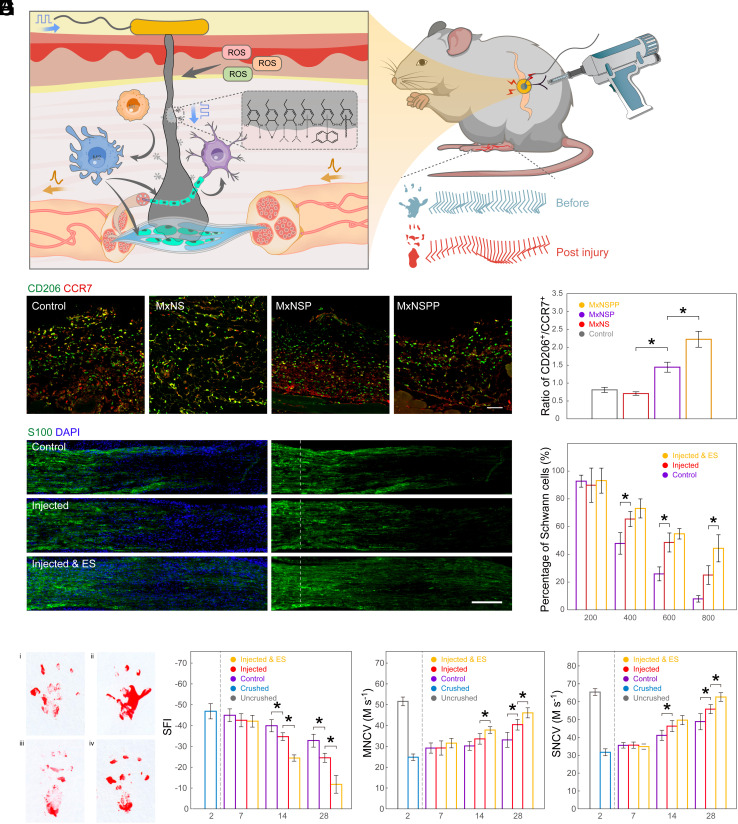
Fig. 3.
Jet-injected neural interface promoted the recovery of motor and sensory nerves in peripheral nerve injury. (A) Injected neural interface regulated immune responses between macrophages, SCs, and neurons, facilitating cellular migration and nerve recovery. (B) Immunofluorescent images of CD206+ (green) CCR7+ (red) macrophages in SNC models injected with different nanosheets or saline as control (Scale bar: 200 µm.) (C) Quantitative analysis of CD206+/CCR7+ macrophages in different groups (n = 3). (D) Immunofluorescent images of S100+ SCs in SNC representative sections (Scale bar: 200 µm.) (E) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of SCs past the crush site normalized to the fluorescence intensity at the crush site plotted as a function of the distance from the crush site (n = 3). (F) Footprint stamps in walking track analysis (i interface injected with ES, ii uncrushed, iii control, and iv interface injected without ES). (G) Quantitative analysis of SFI (n = 5). (G) Motor nerve conduction velocity of SNC mice (n = 5). (H) Motor nerve conduction velocity of SNC mice (n = 5). (I) Sensory nerve conduction velocity. The mice SNC was made on day 0. ES was applied every 2 d since day 2 (n = 5). * indicates a statistical difference (P < 0.05). All statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA.