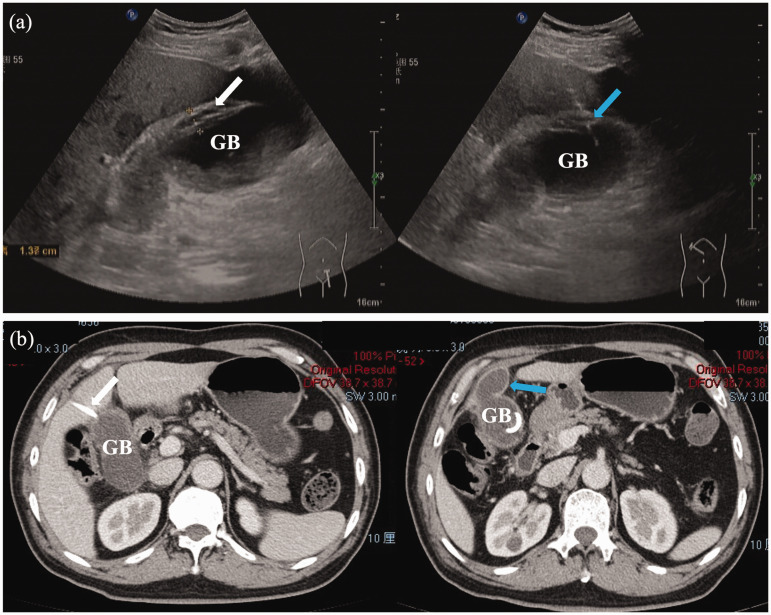
Figure 2.
(a) Images obtained during ultrasound-guided percutaneous gallbladder (GB) drainage performed at the bedside to treat a male patient in his early 60s who presented with 3 days of right upper abdominal pain, showing GB wall oedema (white arrow) and the needle puncturing the GB through the liver parenchyma (blue arrow); and (b) abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography axial plane images obtained 4 days later showing proper positioning of the drainage tube (white arrow) and a decreased amount of fluid around the GB (blue arrow).