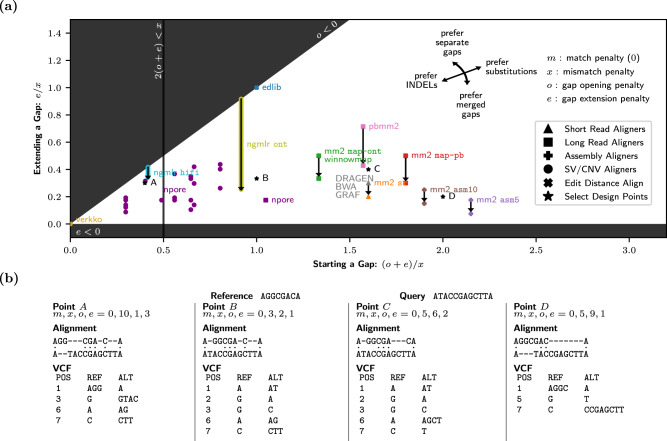
Fig. 2. The affine gap design space for alignment and variant representation.
a The design space for an affine-gap aligner with match, mismatch, gap opening, and gap extension penalties m, x, o, and e. All parameters have been normalized so that m = 0 (see Supplementary Fig. 3 for details), and the penalties for starting (o + e) and extending (e) a gap are plotted relative to substitutions (x). This plot includes the aligners used in the precisionFDA’s Truth Challenge V2, as well as assembly, edit distance, and copy number/structural variant (CNV/SV) aligners for comparison. Each aligner is plotted in a unique color, except for when multiple aligners use identical parameters. For dual affine gap aligners, two points are plotted with an arrow indicating the transition to a lower extension penalty e2. NGMLR26 uses a logarithmic gap penalty, and so there is a continuous lowering of e. nPoRe20 uses different gap penalties for simple tandem repeats (STRs) based on their measured likelihoods, resulting in many plotted points. b Aligning the same query and reference sequence using different gap parameters (design points A, B, C, and D) results in different sets of reported variants. Each variant call file (VCF) shows the variant positions (POS) in addition to the reference (REF) and alternate (ALT) alleles.