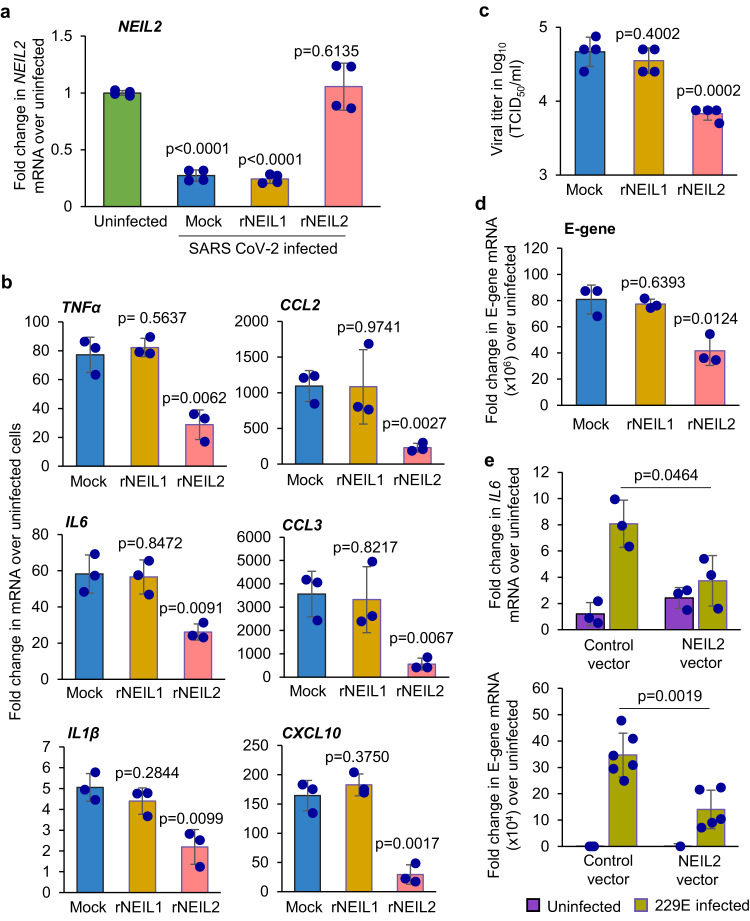
Fig. 4. Effect of rNEIL2 on inflammatory gene expression in A549-ACE2 cells following infection with CoV-2.
a–d A549-ACE2 cells were transduced with mock (PBS+ carrier), rNEIL1 or rNEIL2 proteins for 16–24 h, then infected with SARS-CoV-2 (WA1-2020 at MOI 1). Total RNA was isolated at 24 h post infection and expression of NEIL2 (n = 4 biological replicates generated in 3 independent experiments) (a) and proinflammatory genes (n = 3 independent experiments), as indicated, was analyzed using RT-qPCR (b). Supernatants were harvested at 24 h post-infection for viral titer measurement using standard Vero E6 viral titration assay for the supernatants to determine TCID50/mL and plotted at log10 scale (n = 4 biological replicates generated in 3 independent experiments) (c). Expression of viral E-gene (n = 3 independent experiments) (d) was analyzed by RT-qPCR. e AGS cells transfected with control vector (control-vector) or NEIL2 expressing vector (NEIL2 vector) were infected with 229E strain and expression of host IL6 (n = 3 independent experiments) (upper panel) or viral E-gene (n = 4–6 biological replicates generated in 3 independent experiments) (lower panel) was analyzed using RT-qPCR compared to uninfected cells 72 h post infection. Target mRNA expression was normalized to 18S RNA and represented as fold change over uninfected cells. All error bars represent ± standard deviation from the mean. p-values (unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test) vs. uninfected cells for (a); mock for b–d; and infected control vector expressing cells for (e). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.