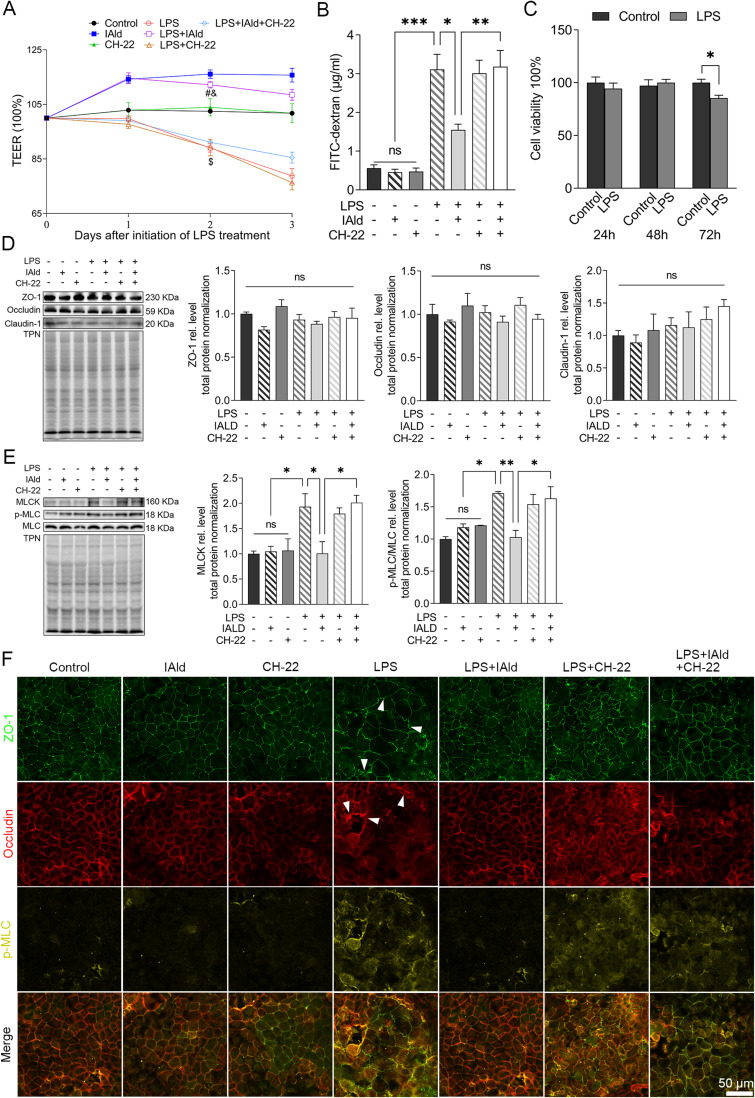
Figure 7.
IAld attenuated Caco-2 epithelial barrier dysfunction through AhR activation.
Notes: Polarized Caco-2 monolayers were pre-treated with or without CH-22 (10 μM) for 1 h before IAld (200 μM) was added to the apical chamber for another 1 h, followed by adding LPS (100 ng/mL) into the basolateral chamber for next 48 h. Epithelial permeability was measured by (A) TEER or (B) FITC-dextran paracellular transport from the apical to basolateral compartment. (C) The cytotoxic effects of LPS on Caco-2 monolayer at different time points were measured. (D and E) The expression of tight junction (TJ) proteins (eg, ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1), and MLCK and p-MLC were determined by immunoblot. Total protein was a loading control. (F) Representative images of immunofluorescent (IF) staining of TJ and p-MLC in Caco-2 monolayer. Arrows, the disrupted phenotypes of TJ proteins in LPS-stimulated Caco-2 monolayer. All data obtained from IF was quantified using Image J. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; #p < 0.001 versus LPS; &p < 0.01 versus CH-22; $p < 0.001 versus Control.
Abbreviation: ns, statistically non-significant.