Figure 2. Schematic representation of the NLRP3 activation and the subsequent NLRP3 inflammasome formation.
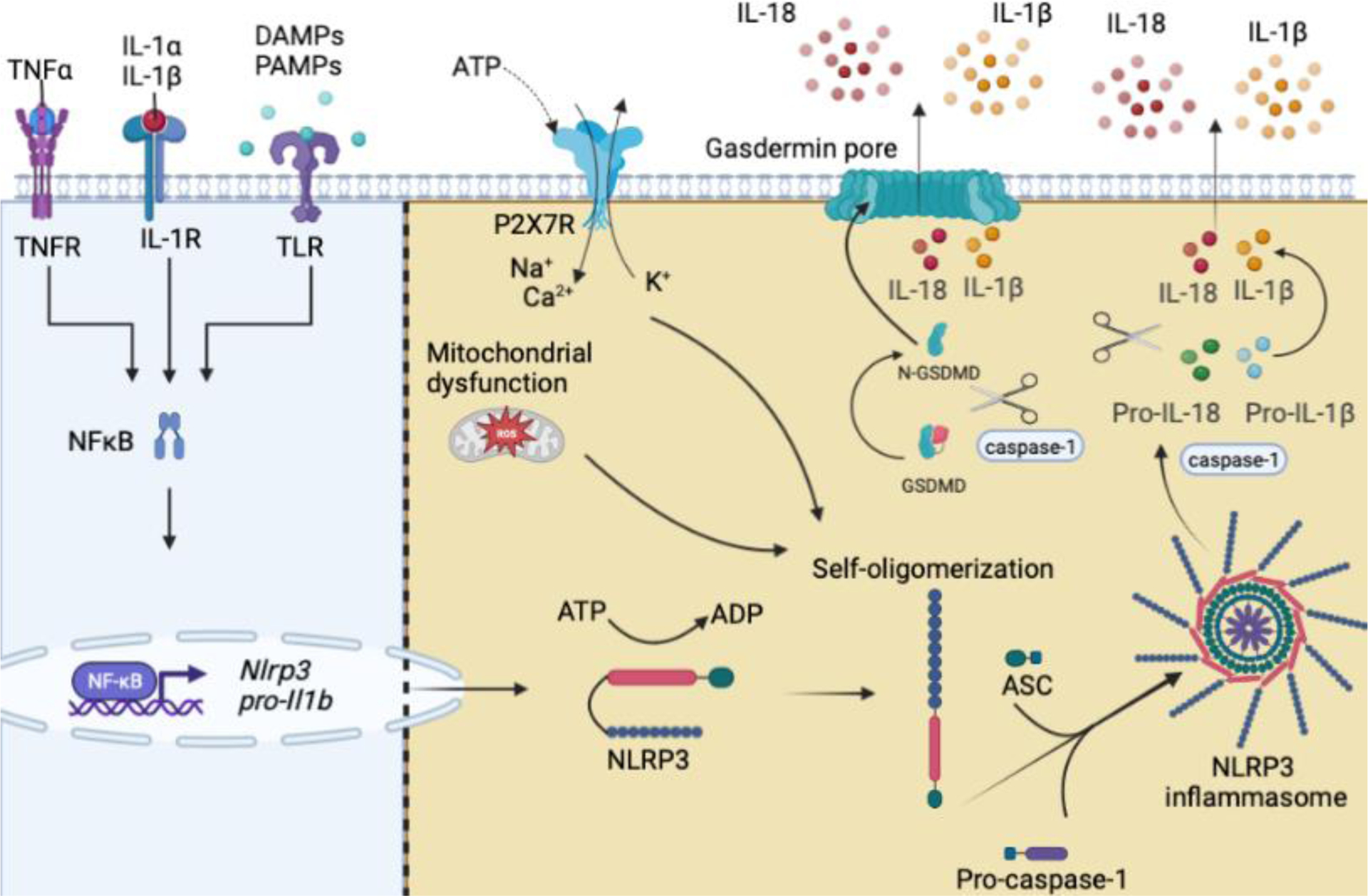
(Left) Engagement of TLRs by PAMPs and DAMPs or cytokine receptors by their respective cytokines (IL-1α, IL-1β, or TNFα) lead to upregulation of NFκB-mediated gene expression of inflammasome components, termed priming. (Right) Activation occurs through PAMPs and DAMPs that activate upstream signals resulting in NLRP3 self-oligomerization (in text). NLRP3 then interacts with ASC, pro-caspase-1 is recruited resulting in caspase-1 activation, activated caspase-1 then cleaves pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18. Biologically active IL-1β and IL-18 are then secreted into the extracellular space. Abbreviations: interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin 1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1), tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR), toll-like receptor (TLR), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPS), ATP (adenosine triphosphate), ADP (adenosine diphosphate), GSDMD (gasdermin D), purinergic receptor P2X7 (P2X7R), nuclear factor-κB (NFκB), reactive oxygen species (ROS), apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC).
