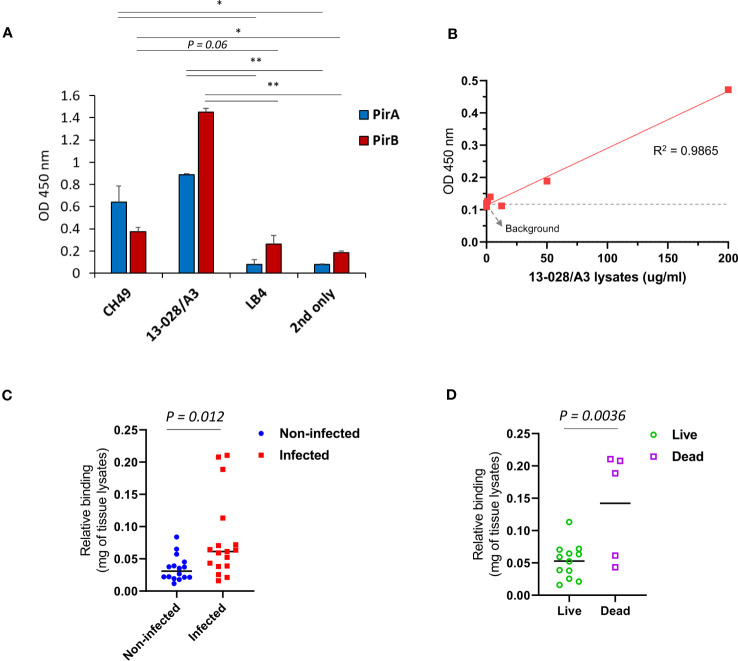
Figure 5.
Detection of PirABVp in shrimps infected by V. parahaemolyticus 13-028/A3. (A) Detection of the toxin subunits from the culture lysate of 13-028/A3 strain. Total proteins were extracted from the pellet of cultured bacteria and coated on an ELISA plate; the expression of PirA and PirB was determined by 1A8 and 3A5, respectively. CH49 and LB4 strains were used as a PirA/PirB-positive and -negative controls, respectively. Values represent the mean ± SD for a duplicate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (B) Assessment of detection sensitivity of PirABVp in 13-028/A3 lysate. The culture lysate was serially diluted and the detection sensitivity (LoD) was determined estimated as 13.5 ug/mL. (C, D) Detection of PirABVp complex in shrimps infected with 18-028/A3 strain. At day 7 after infection, hepatopancreas from non-infected or infected shrimps were dissected and lysed to prepare protein lysates. PirABVp complex in the lysates was significantly detected in the infected group, but not in the non-infected group. The immunoassay showed a significant detection of PirABVp complex from dead shrimps compared to live shrimps in the infected group.