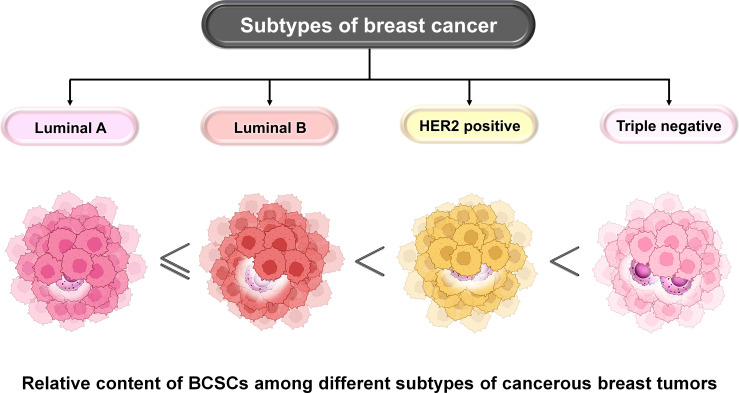
Figure 4.
Relative content of BCSCs among different subtypes of BC. The proportion of BCSCs varies among different subtypes of BC and this correlates with their prognosis. Luminal A has the lowest proportion followed by luminal B, HER2+, and TNBC subtypes of BC. The landscape of developing TME involves infiltration, adaptation, and/or alteration as well as crosstalk-dependent cellular evolution involving cancer cells, immune cells, and the extracellular matrix (ECM), which altogether determines the fate of the tumor. A significant body of evidence suggests that a bidirectional crosstalk is involved in developing TME. On the one hand, immune cells of the TME modulate stemness in BC cells, and on the other hand, cancer cells escape immune surveillance by exercising their effects on cells like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), dendritic cells (DCs), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), T regulatory (Treg) cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). The co-evolution of the TME and BCSCs determines the fate of BC.