Figure 3.
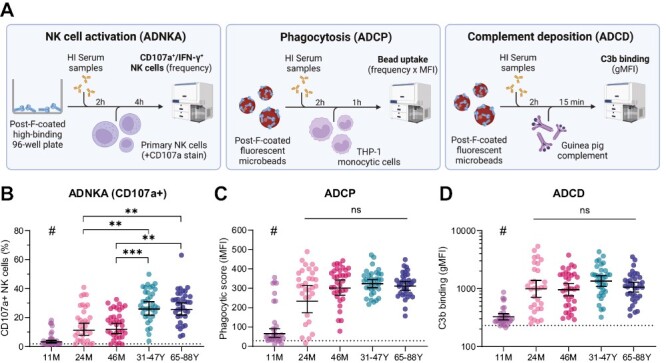
Fc-mediated antibody effector functions in different age groups. (A) Schematic overview of the methods used to assess ADNKA, ADCP, and ADCD in serum from 11-month (n = 33), 24-month (n = 31), and 46-month-old children (n = 35), adults (n = 35), and older adults (n = 35). (B) ADNKA with percentage of CD107a + NK cells as read-out; the average of three healthy NK cell donors is depicted for each participant. (C) ADCP by THP-1 cells with phagocytic score as read-out; data for each participant consists of the average of technical duplicates. (D) ADCD with gMFI as read-out; data for each participant consists of the average of technical duplicates. The dotted lines indicate the level of the negative control. All data points represent individual participants and geometric means with 95% confidence intervals are depicted. Data is analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis test. # indicates statistical significance of at least P < 0.01 compared to all other age groups. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant. ADCD: antibody-dependent complement deposition; ADCP: antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; ADNKA: antibody-dependent NK cell activation; gMFI: geometric mean fluorescence intensity; HI: heat-inactivated; iMFI, integrated mean fluorescence intensity; NK cells: natural killer cells.
