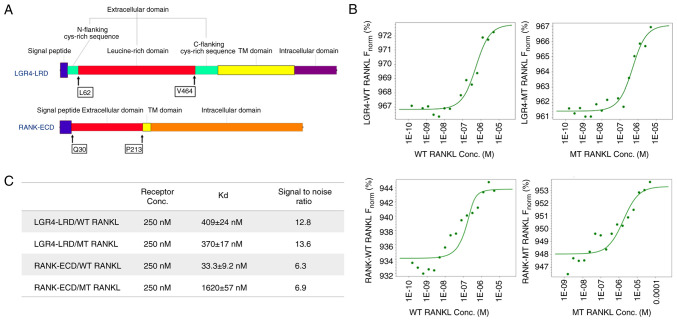
Figure 1.
Suitability of microscale thermophoresis as a sensitive method was presented to determine WT RANKL and MT RANKL binding affinities. (A) Protein sequences of the LGR4 and RANK receptor proteins used in the present study. The LGR4 receptor sequence from L62 to V464 is the extracellular domain that represents the ligand-binding domain. The ligand-binding domain of RANK is from Q30 to P213. (B) Concentration of WT RANKL/MT RANKL used in titration experiments ranged from 11.5 nM to 50 μM, and the concentration of the labeled LGR4 and RANK receptors was constant at 250 nM. The y-axis shows affinity analysis data using Frobenius normalization [F norm (%)]. (C) Binding affinities (Kd values) of LGR4 and RANK to WT RANKL and MT RANKL. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of each data point calculated from three independent thermophoresis measurements. Kd, dissociation constant; LGR4, leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 4; MT, mutant; RANK, receptor-activated nuclear factor-κB; RANKL, RANK ligand; WT, wild-type; ECD, extracellular domain; LRD, leucine rich domain.