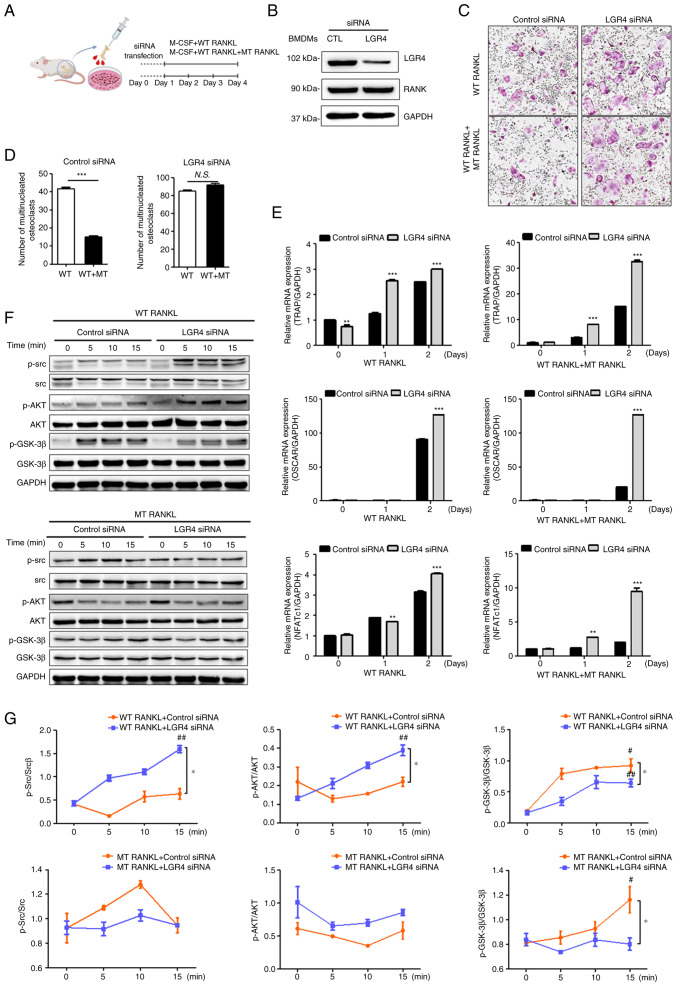
Figure 2.
Effect of MT RANKL on osteoclast differentiation in vitro. (A) Schedule for treating control or LGR4 siRNA-transfected BMDMs with WT RANKL or WT RANKL + MT RANKL. (B) Western blotting of LGR4 and RANK expression in LGR4 siRNA-transfected BMDMs. LGR4 expression was markedly lower in LGR4 siRNA-treated BMDMs. (C) A representative image of BMDMs stained for TRAP (red) following treatment of control siRNA- or LGR4 siRNA-transfected BMDMs with WT RANKL (75 ng/ml) or WT RANKL (75 ng/ml) + MT RANKL (75 ng/ml). Magnification, ×100; scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Number of multinucleated TRAP-positive cells (≥3 nuclei). ***P<0.001. (E) Osteoclast-related gene expression in control siRNA- or LGR4 siRNA-transfected BMDMs. BMDMs were exposed to WT RANKL (75 ng/ml) or WT RANKL (75 ng/ml) + MT RANKL (75 ng/ml) for 2 days. Gene expression was determined by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and normalized to the expression of GAPDH. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs. Control siRNA. (F) Western blot analysis of RANK and LGR4 signaling cascades in control siRNA- or LGR4 siRNA-transfected BMDMs in the presence of WT RANKL (2 μg/ml) or MT RANKL (2 μg/ml). GAPDH was used as a loading control. BMDM, bone marrow-derived macrophage. (G) Densitometric value of p-Src/Src, p-AKT/AKT and p-GSK-3β/GSK-3β, as determined by western blot analysis. Results are representative of three separate experiments that had comparable results. *P<0.05 Control siRNA vs.LGR4 siRNA at 15 min; #P<0.05 vs. WT RANKL + Control siRNA at 0 min, ##P<0.05 vs. MT RANKL+ Control siRNA at 0 min. GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; LGR4, leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 4; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MT, mutant; NFATc1, nuclear factor of activated T cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1; N.S., not significant; p-, phosphorylated; RANK, receptor-activated nuclear factor-κB; RANKL, RANK ligand; siRNA, small interfering RNA; TRAP, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase; WT, wild-type.