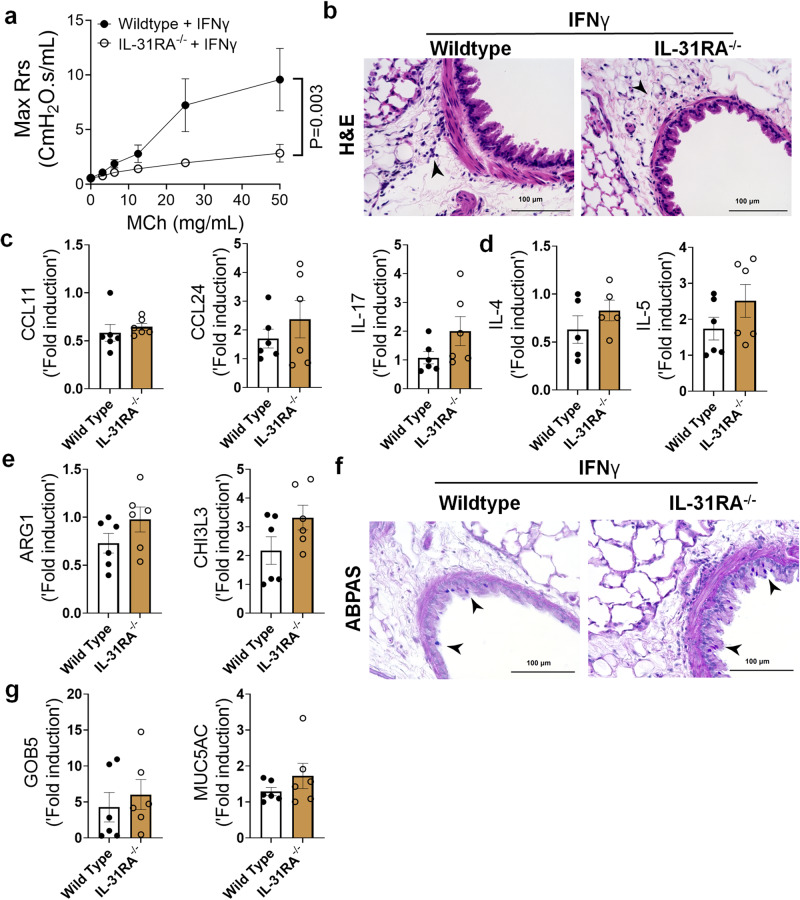
Fig. 8. Loss of IL-31RA is sufficient to attenuate IFNγ-induced AHR with no effect on inflammation and goblet cell hyperplasia.
a Wildtype (n = 9) and IL-31RA–/– (n = 9) mice were treated intratracheally with IFNγ (5 μg) on days 0 and 6, and resistance was measured with increasing doses of MCh using Fexivent. Data are shown as mean SEM. Two-way ANOVA was used. b Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections from wildtype (n = 6) and IL-31RA–/– (n = 6) mice treated with IFNγ. Images were captured at ×20 magnification. Scale bar, 100 µm. c, d, e Quantification of inflammatory cytokines (CCL11, CCL24 and IL-17), Th2 cytokines (IL-4 and IL-5), and Th2 response-associated genes including ARG1, and CHl3L3 in the lungs of wildtype (n = 6) and IL-31RA–/– (n = 6) mice treated with IFNγ. Data are shown as mean SEM. Unpaired t test was used, and no statistical signification observed between groups. f Representative images of Alcian blue periodic acid-Schiff-stained lung sections from wildtype (n = 6) and IL-31RA–/– (n = 6) mice treated with IFNγ. Images were captured at ×20 magnification. Scale bar, 100 µm. g Quantification of mucus-associated genes including GOB5 and MUC5AC transcript levels in the lungs of wildtype (n = 6) and IL-31RA–/– (n = 6) mice treated with IFNγ. Data are shown as means SEM. Unpaired t test was used, and no statistical signification observed between groups. At least two independent experiments produced similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.