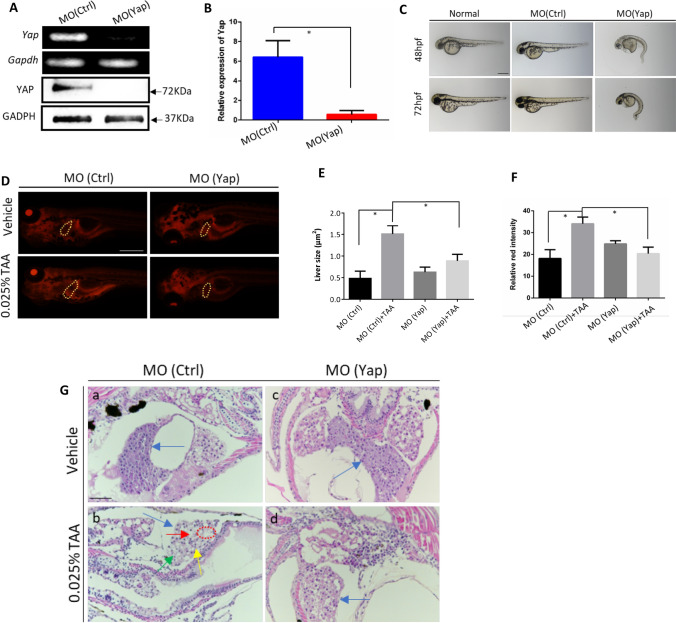
Fig. 1.
Analysis of morphant phenotype and TAA-induced embryonic liver lesions caused by Yap knockdown. A Validation of Yap knockdown by RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. Total RNA and proteins were extracted from 24 hpf zebrafish embryos in MO (Yap) and MO (Ctrl) (n = 10). B Validation of Yap knockdown by qPCR. C Morphant observation of 48 and 72 hpf embryos injected with MO (Yap) (5 ng/embryo), MO (Ctrl) (5 ng/embryo), and non-injected normal embryos. D Nile red-stained sections of embryos with the treatment of 0.025% TAA from 72 hpf to 7 dpf. E Qualifications of liver size in each group, n = 5. F Qualifications of Nile red staining by relative red intensity by ImageJ (n = 5). Data are shown as means ± SEM. *p < 0.05. G Histological evaluations of zebrafish liver by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) with the treatment of 0.025% TAA from 72 hpf to 7 dpf