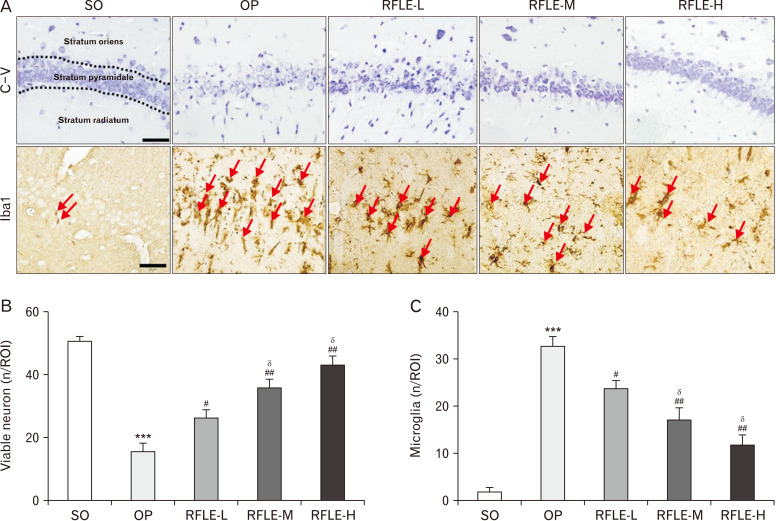
Fig. 4.
Effects of RFLE on neuronal viability and microglial activation in hippocampal CA1 of the VaD rat. (A) Representative photographs of cresyl violet stained (top row) and Iba1-immunostained (bottom row) hippocampal CA1 tissues. Iba1-immunopositive microglia are indicated with red arrows. Scale bar=50 μm. (B) Quantitative graphs showing the number of viable pyramidal neurons and (C) microglia. In graphs, values are presented as mean±SEM (***P<0.001 vs. SO; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 vs. OP; δP<0.05 vs. RFLE-L). RFLE, Rubus fruticosus leaf extract; SO, sham operation; OP, operation; RFLE-L, operated and treated with low dose (30 mg/kg) of RFLE; RFLE-M, operated and treated with medium dose (60 mg/kg) of RFLE; RFLE-H, operated and treated with high dose (90 mg/kg) of RFLE; C-V, cresyl violet; Iba1, ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1; ROI, region of interest.