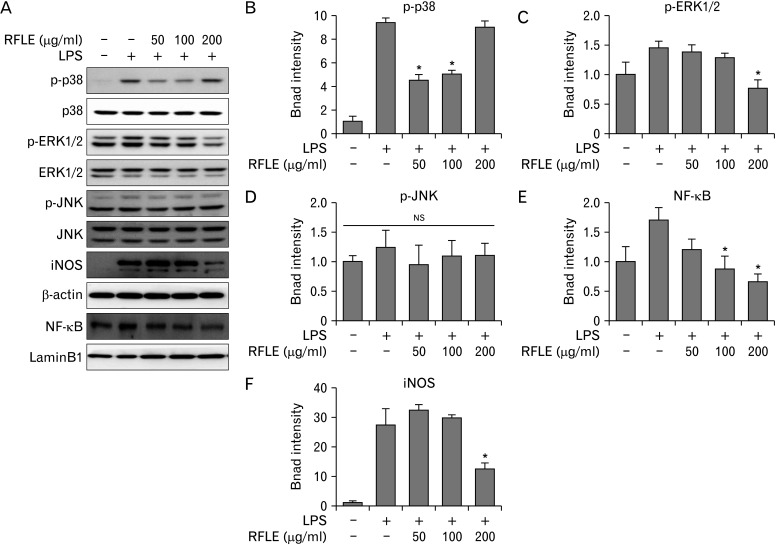
Fig. 6.
Effect of RFLE on MAPK/NF-κB/iNOS signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged BV-2 cells. BV-2 cells were pretreated with the different dose of RFLE for 6 hours and further treated with 1 μg/ml LPS for 18 hours. (A) Representative western band images and (B–F) the quantitative graphs of p-p38, p-ERK1/2, p-JNK, nuclear NF-κB, and iNOS. The band intensities of p-p38, p-ERK1/2, p-JNK, and iNOS were normalized by β-actin. NF-κB intensity was normalized by laminB1, the internal controls. Data were expressed as fold of the controls (RFLE- and LPS-untreated) and collected from at least three independent experiments. Values are presented as mean±SEM (*P<0.05 vs. RFLE-untreated and LPS-treated). RFLE, Rubus fruticosus leaf extract; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; NS, not significant.