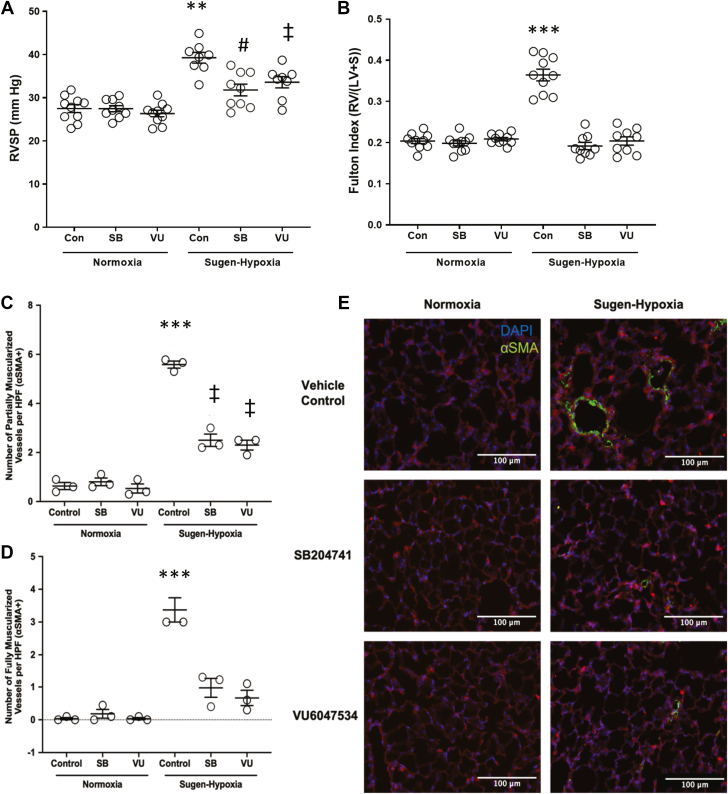
Figure 2.
Targeting the 5-HT2B Receptor Prevents Elevated RVSP and Fulton Index in Experimental Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
(A) 5-HT2B ligands, SB204741 (SB) and VU6047534 (VU) , prevent right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) elevation compared with nondrug-treated mice exposed to Sugen-hypoxia. (B) SB204741 and VU6047534 prevent elevated Fulton Index in mice exposed to Sugen-hypoxia. (C to E) Animals exposed to Sugen-hypoxia have significantly more muscularized vessels (0- to 25-μm diameter) than normoxic control animals, and SB204741 and VU6047534 significantly reduce the number of partially and fully muscularized vessels in Sugen-hypoxia exposed animals. Data presented as mean ± SEM. ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs all other experimental groups; #P < 0.05 vs control and VU6047534 normoxia groups; and ‡P < 0.01 vs normoxia groups. All statistics analyzed with 2-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey post hoc
test for multiple comparisons. HPF = high-powered field; LV = left ventricle; RV = right ventricle; S = septum; SMA = smooth muscle actin.