Fig. 1. Brain mosaic copy number gain of chromosome 1q.
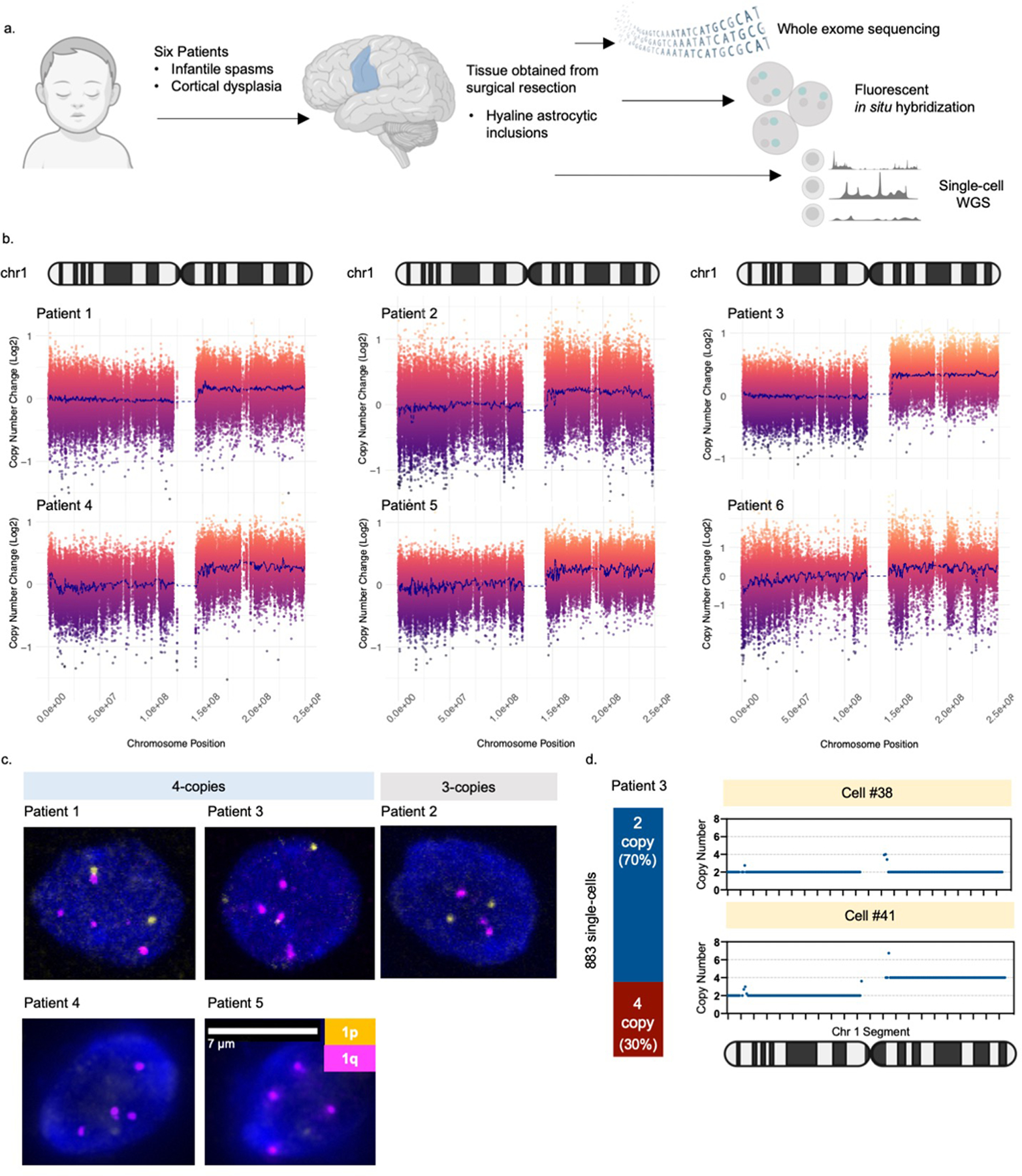
(A) Six patients included in the study met the following criteria: infantile spasms progressing to intractable focal epilepsy, cortical dysplasia, and hyaline astrocytic inclusions. Tissue obtained from surgical resection was evaluated for mosaicism using whole exome sequencing, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), and single-cell whole genome sequencing. (B) Copy number analysis of exome sequencing data comparing brain tissue to a matched blood sample from each patient. Each patient had a non-integer (i.e., mosaic) gain encompassing almost the entire long arm of chromosome 1 (1q21-q44). (C) Representative examples of FISH analysis of patient brain cells showing three or four copies of chromosome 1q present in each cell. Cells with 1q gain were observed on at least 3 slides per patient. (D) Copy number profiling of single-nuclei from Patient 3 brain tissue confirming the presence of chromosome 1q tetrasomy in approximately 30% of nuclei.
