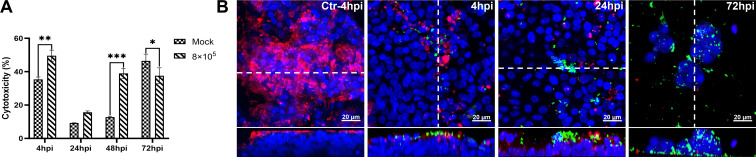
Fig 1.
Cytotoxicity and T. pyogenes-induced damage to well-differentiated porcine bronchial epithelial cells. PBECs were apically infected with approximately 8 × 105 CFU of T. pyogenes and washed thoroughly after 4 h to remove non-adherent bacteria, then further incubated under ALI conditions. (A) Cytotoxic effects of T. pyogenes on PBECs grown under ALI conditions were quantified by a standard LDH-release assay. Results are expressed as percent cytotoxicity compared to 100% killed cells condition and expressed as mean ± SD; *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < 0.001, determined using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Experiments were performed three times. (B) Immunostaining was performed to visualize cilia (red) and T. pyogenes (green), and nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). Bars represent 20 µm in horizontal sections for upper images, and lower images are the orthogonal views of Z-stacks (white dotted line) as shown in YZ sections at 4 and 72 hpi or XZ sections in control (Ctr) at 4 and 24 hpi.