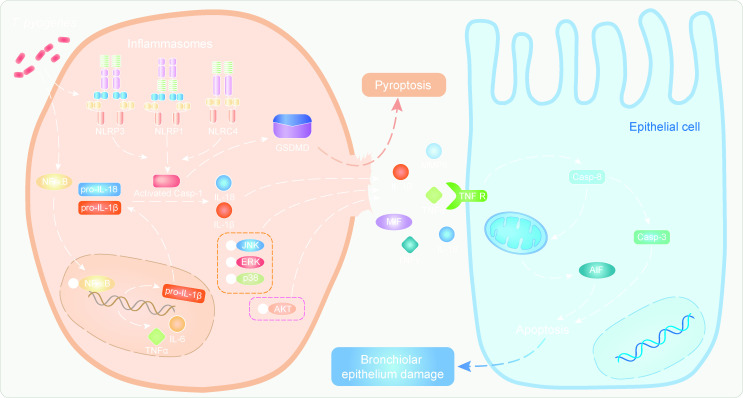
Fig 10.
A schematic overview summarizing the main mechanism of epithelial cell injury. T. pyogenes infection triggers NF-κB to enter the nucleus, where it promotes the expression of pro-inflammatory factors and NLR inflammasomes. Meanwhile, T. pyogenes can directly promote the assembly and formation of the NLR inflammasome. Pyroptosis happens via the NLR-ASC-caspase-1-GSDMD pathway, which promotes the release of mature IL-18, IL-1β, and other pro-inflammatory factors into the extracellular space, which can cause inflammatory lung tissue injury. For example, TNF-α increases and induces epithelial cell apoptosis via the TNF receptor pathway.