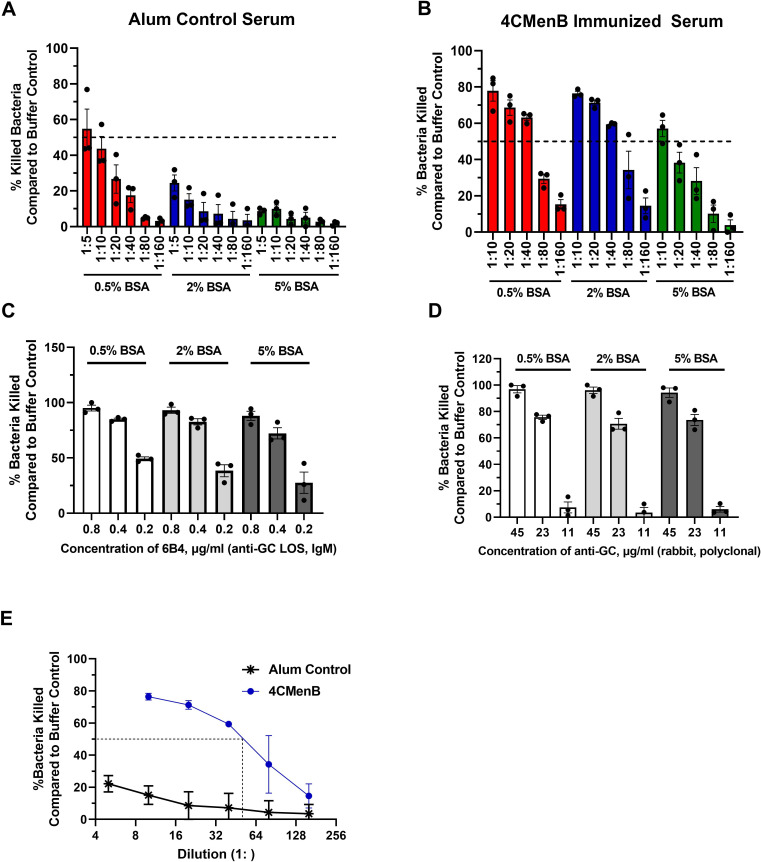
Fig 6.
Serum bactericidal activity elicited by 4CMenB vaccination against N. gonorrhoeae. (A and B) N. gonorrhoeae strain FA1090 was incubated with the indicated concentrations of BSA in the presence of the indicated dilution of pooled serum from alum-treated (A) or 4CMenB-vaccinated (B) mice. Serum bactericidal activity was measured using 2% Ig-depleted NHS as complement source and reported as percent bacteria killed relative to the buffer control. (C and D) N. gonorrhoeae strain FA1090 was mixed with the indicated concentration of BSA and 6B4 (C) or rabbit anti-N. gonorrhoeae (GC) antibody (D). The percentage of bacteria killed relative to buffer control was calculated as in A and B. Based on the results, 2% Ig-depleted NHS, 2% BSA, and 0.4 µg/mL 6B4 or 22.5 µg/mL rabbit anti-N. gonorrhoeae antibody were selected as positive control conditions for FA1090 N. gonorrhoeae; similar calculations were made for other N. gonorrhoeae strains with the positive control antibodies in Table 2. (E) SBA activity measured using strain FA1090 N. gonorrhoeae, 2% BSA, the indicated dilutions of pooled serum from 4CMenB-vaccinated (circle) or alum-treated control (asterisk) mice, and 2% Ig-depleted NHS. SBA titers for all five strains of N. gonorrhoeae are reported in Table 2. Bars indicate the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, with each biological replicate as one data point.