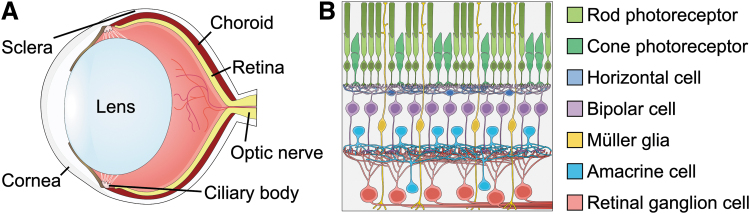
FIG. 1.
The retina is the light-sensing tissue of the eye. (A) Light passes through the cornea and is focused by the lens to strike the retina, which sits at the back of the eye. (B) Light is detected by photoreceptors, and information about the visual field is passed through horizontal, bipolar, and amacrine interneurons, then to RGCs, which transmit this information to the brain via the optic nerve. RGC, retinal ganglion cell.