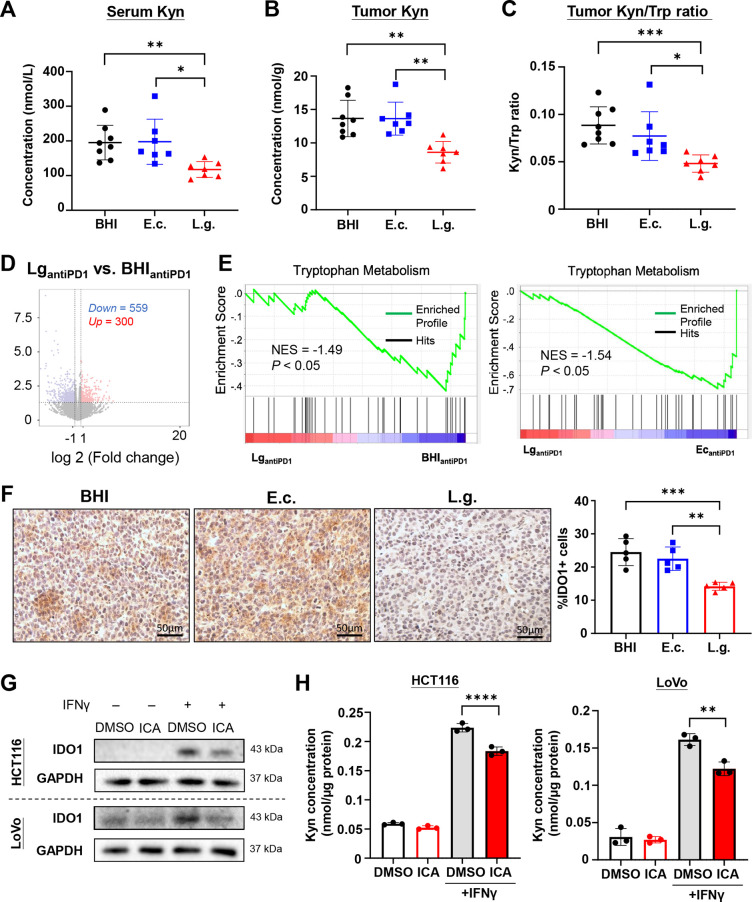
Figure 5.
Lactobacillus gallinarum and ICA inhibited IDO1 expression and Kyn production in tumour. L. gallinarum reduced (A) serum Kyn level, (B) tumour Kyn level, (C) Kyn/Trp ratio in tumours in MC38 syngeneic mouse model. (D) RNA sequencing revealed a differential gene expression between BHI plus anti-PD1 group versus L. gallinarum plus anti-PD1 group. (E) Enrichment plot of Trp metabolism pathway. (F) Immunohistochemical staining of IDO1 in tumour tissues of CT26 syngeneic mouse model. Scale bar=50 µm. (G) ICA (5 µM) significantly inhibited IDO1 expression in HCT116 and LoVo cell lines. IFNγ (100 ng/mL) was added 1 day after ICA/DMSO treatment to induce IDO1 expression. (H) ICA (5 µM) reduced Kyn level in HCT116 and LoVo cell lysates, as detected by Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, after normalisation of protein concentration. IFNγ (100 ng/mL) was added to induce IDO1 expression. Statistical significance was determined by Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. E.c., E. coli; ICA, indole-3-carboxylic acid; IDO1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; Kyn, kynurenine; L.g., L. gallinarum; Trp, tryptophan.