FIG. 1.
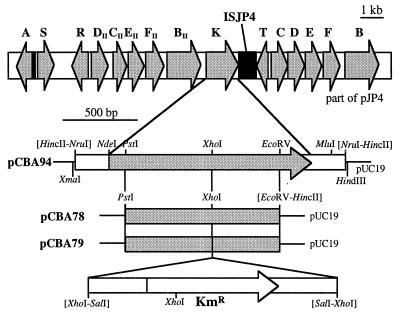
(Top) Overview of the genetic organization on plasmid pJP4. Arrows, positions and orientations of the various tfd genes; black boxes, ISJP4 DNA. (Bottom) Restriction maps of plasmids used in this study. Plasmid pCBA94 contains a 1.9-kb NruI fragment of pJP4 in pUC19 (29). The sequence of this DNA fragment is presented in Fig. 2. Plasmid pCBA78 contains a 1.1-kb PstI-EcoRV fragment of tfdK in pUC19. A 1.7-kb SalI fragment carrying the kanamycin cassette from plasmid pUT/Km (12) was inserted into the XhoI site of pCBA78, resulting in plasmid pCBA79. The latter was used to construct a tfdK mutant of R. eutropha JMP134(pJP4). pUC-derived plasmids were propagated in cells of E. coli DH5α (23) cultivated at 37°C on Luria broth medium (23) in the presence of 100 μg of ampicillin per ml.