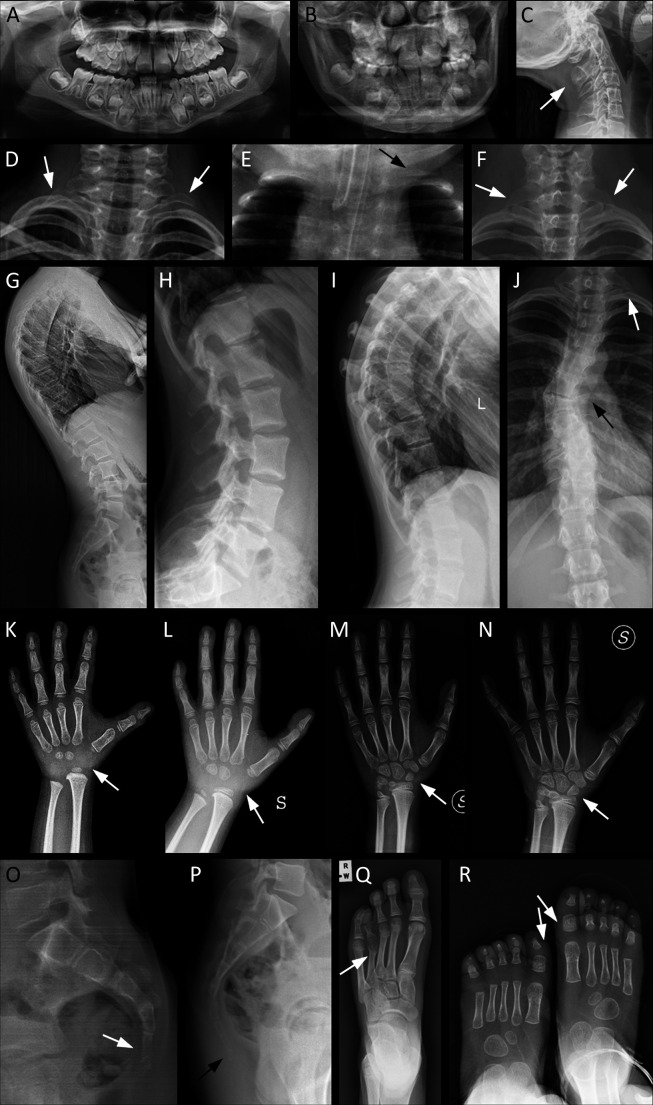
Figure 2.
Main radiological characteristics of selected patients from our cohort, representative of the skeletal features of KBG syndrome. Arrows indicate the most relevant details. (A) Pt. 10: orthopantomography showing macrodontia of the permanent upper incisors and dental crowding. (B) Pt. 32: macrodontia of the permanent upper incisors, dental crowding. (C) Pt. 1: cervical C2/C3 vertebral fusion. (D) Pt. 21: bilateral cervical ribs. (E) Pt. 12: supernumerary cervical rib on the left side. (F) Pt. 10: bilateral C7 hypertrophic transverse process. (G) Pt. 26: thoracic hyperkyphosis. (H–J) Spinal column anomalies of Pt. 39: tall lumbar vertebral bodies (H), kyphosis (I), left cervical rib and scoliosis due to thoracic hemivertebrae (J). (K–N) Evolution of the main anomalies of hand bones over time: delayed carpal ossification with absence of the proximal row at about 3 years (K) and 6 years of age (L); partial fusion of the lunate and triquetral carpal bones at 9 years (M); complete fusion of the lunate and triquetral bones at 10 years (N). (O) Pt. 32: agenesis of the coccyx: only the outline of the first coccygeal vertebra is present. (P) Pt. 26: supernumerary coccygeal vertebrae. (Q) Pt. 13: short and dysmorphic metatarsal and phalanges of fourth ray, bilaterally (right foot not shown). (R) Pt. 12: broad and short metatarsal and phalanges of first ray, bilaterally. Pt., participant.