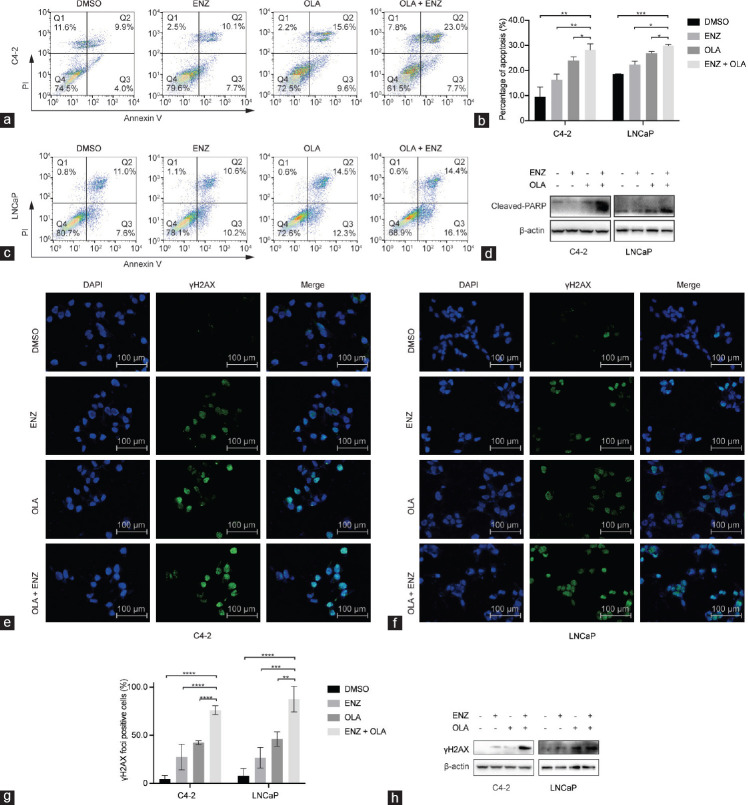
Figure 2.
Combined treatment of ENZ and OLA induces apoptosis by increasing DNA damage in AR-positive prostate cancer cell lines. (a) The representative dot plots of C4-2 cells treated with DMSO, ENZ (25 µmol l−1), OLA (50 µmol l−1), or their combination for 48 h. (b) The histogram of apoptotic rates was shown after Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. (c) The representative dot plots of LNCaP cells treated with DMSO, ENZ (5 µmol l−1), OLA (30 µmol l−1), or their combination for 48 h. (d) The expression of cleaved-PARP after indicated treatments monitored by Western blot. Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of γH2AX in (e) C4-2 and (f) LNCaP cells treated as indicated for 48 h, and cell nuclei were stained with DAPI. (g) The percentage of cells with γH2AX foci. (h) The expression of γH2AX after indicated treatments monitored by Western blot. Mean with s.d. for three independent experiments is shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (ANOVA). AR: androgen receptor; ENZ: enzalutamide; OLA: olaparib; cleaved-PARP: cleaved-poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase; γH2AX: gamma H2A histone family member X; s.d.: standard deviation; Q1–4: quadrant 1–4; ANOVA: analysis of variance; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide; PI: prodium iodide.