Figure 1: The four pillars of the quadrangle to tackle the burden of stroke: surveillance, prevention, acute care, and rehabilitation.
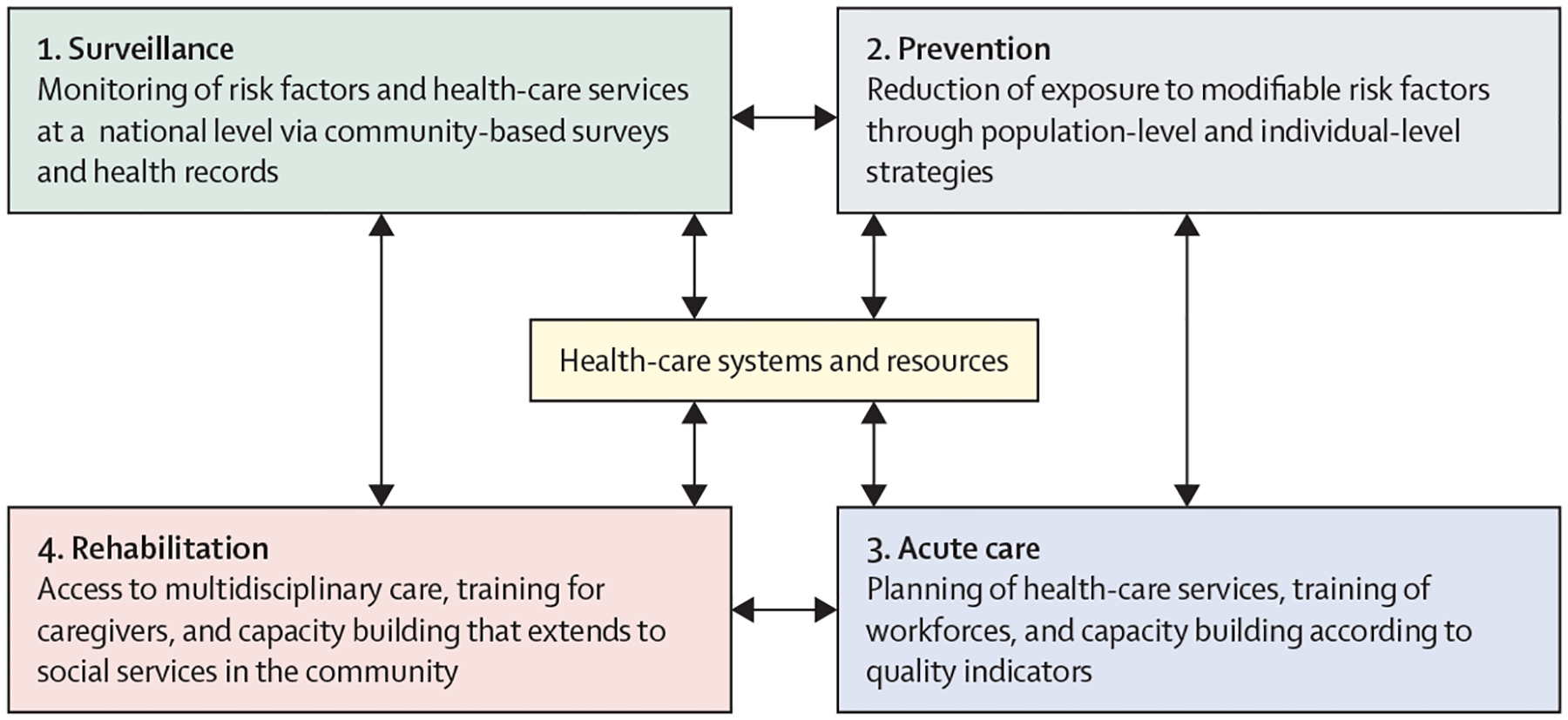
Surveillance strategies include establishing a framework for regular monitoring and assessment of the burden of stroke and its risk factors, and of health-care services at a national level via community-based surveys, data linkage, and electronic health records. These strategies provide the necessary evidence for planning and monitoring prevention, acute care, and rehabilitation interventions. Primordial, primary, and secondary prevention involve implementation of integrated population-wide strategies to reduce modifiable risk factors, such as hypertension and diabetes. Prevention strategies can reduce the incidence, mortality, and prevalence of stroke, and people who develop stroke benefit from secondary prevention (in addition to acute care). Acute stroke care should result in early diagnosis and involves evidence-based management that reduces mortality and improves functional outcomes. Finally, rehabilitation services provide interdisciplinary care for stroke survivors, with the aim of reducing disability-adjusted life-years and improving quality of life. Adapted with permission from Owolabi et al, 2023.11
