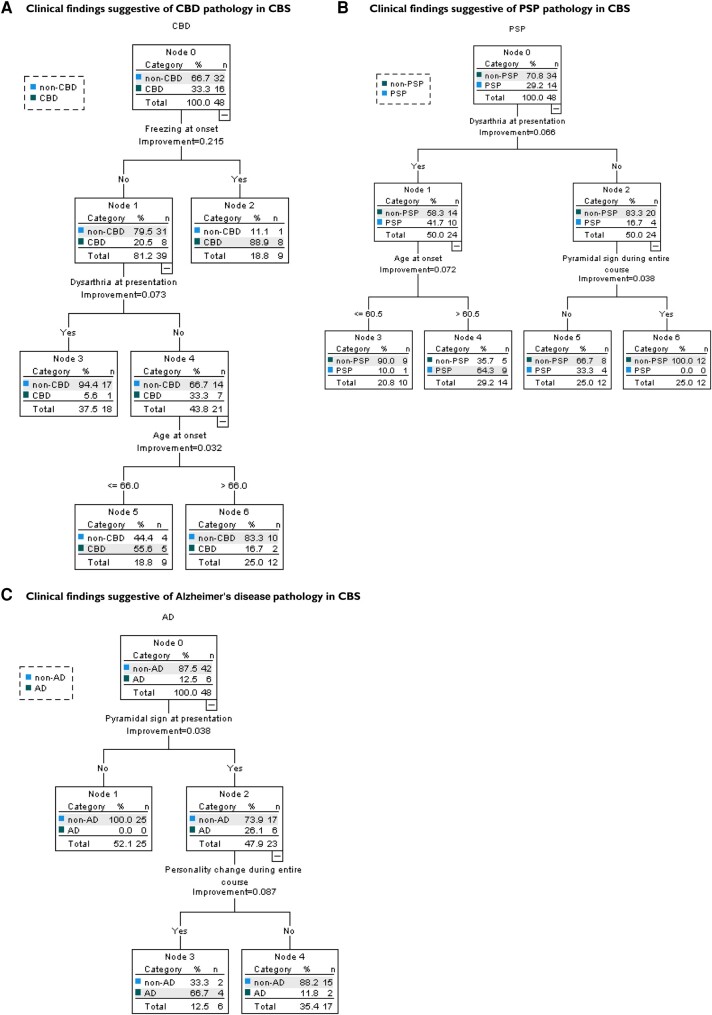
Figure 5.
Decision tree analysis for background pathology of CBS. A decision tree analysis was performed using the classification and regression tree method with CBD, PSP and AD as the dependent variables and sex, age at onset and significant findings (freezing at onset, tremor at onset, dysarthria at onset, dysarthria at presentation, pyramidal signs at presentation, pyramidal signs during the entire course, myoclonus during the entire course, personality change during the entire course and supranuclear gaze palsy during the entire course) as the independent variables, and cross-validation was performed. (A) Clinical findings suggestive of CBD pathology. ‘Freezing at onset’ or ‘no dysarthria at presentation and age at onset <66 years in the case without freezing at onset’ predicted CBD pathology with a sensitivity of 81.3%, specificity of 84.4%, PPV of 72.3% and NPV of 90%. (B) Clinical findings suggestive of PSP pathology. ‘Dysarthria at presentation and age at onset older than 61 years’ suggested PSP pathology, with a sensitivity of 64.3%, specificity of 85.3%, PPV of 64.3% and NPV of 85.3%. (C) Clinical findings suggestive of AD pathology. ‘Pyramidal sign at presentation and personality change during the entire course’ implied AD pathology with a sensitivity of 66.7%, specificity of 95.2%, PPV of 66.7% and NPV of 95.2%. n, number of patients; CRT, classification and regression tree method; CBS, corticobasal syndrome; CBD, corticobasal degeneration; PSP, progressive supranuclear palsy; AD, Alzheimer's disease; PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value.